Uranium-235: The Key to Nuclear Power and Weighted Global Security
Uranium-235: The Key to Nuclear Power and Weighted Global Security
From powering entire nations to shaping the delicate balance of global military power, uranium-235 stands at the heart of modern energy and defense. This rare, fissile isotope drives nuclear reactors that supply nearly 10% of the world’s electricity and fuels sophisticated arsenals worldwide. Its unique nuclear properties—enabling sustained chain reactions—make it both a cornerstone of clean energy innovation and a focal point in nuclear non-proliferation debates.
Understanding uranium-235 means unraveling the dual nature of atomic science: a promise of sustainable power intertwined with complex geopolitical stakes.
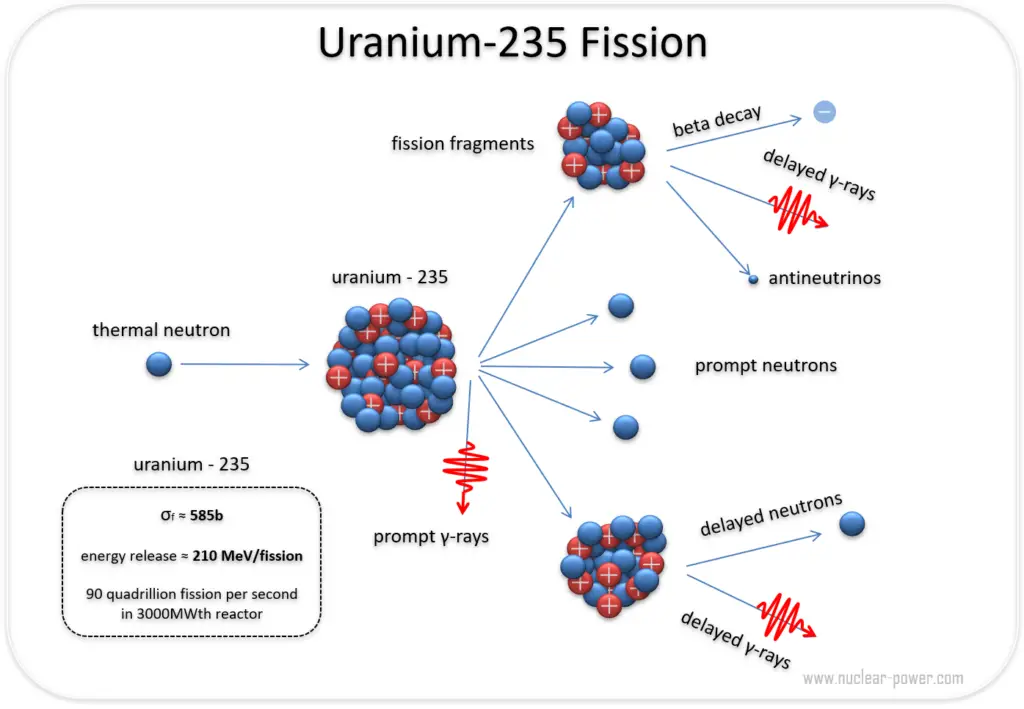
At the core of uranium-235’s utility is its fissile nature—unlike most thorium-232 or natural uranium-238, which resist immediate chain reactions, uranium-235 readily splits when struck by a low-energy neutron. This characteristic allows it to sustain a chain reaction, the fundamental principle behind nuclear reactors and atomic bombs.
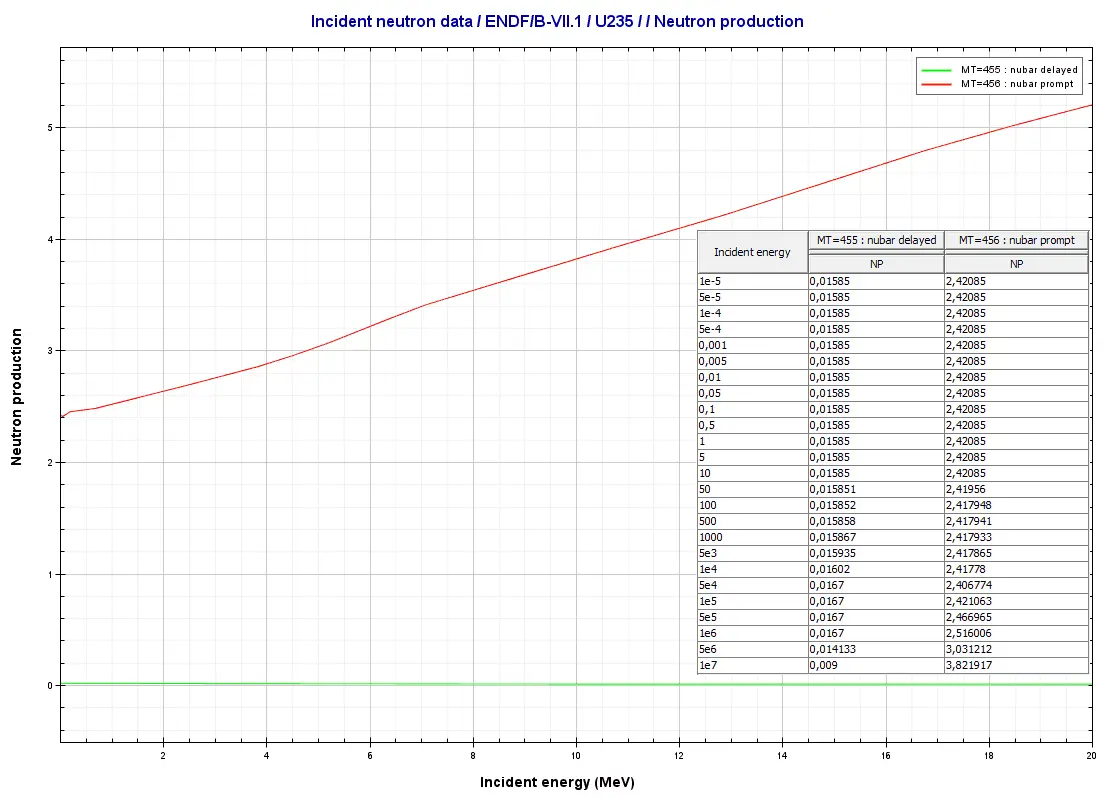
When a single neutron hits a U-235 nucleus, it fractures, releasing an average of 200–240 additional neutrons per fission event. These neutrons can then trigger further splits, multiplying energy output exponentially. “Each fission in a uranium-235 chain release is like a microexplosion—efficient, powerful, and precisely harnessed,” explains Dr.
Elena Markov, a nuclear physicist at the International Atomic Energy Agency. This controlled chain reaction powers commercial reactors, producing heat that drives turbines and generates carbon-free electricity.
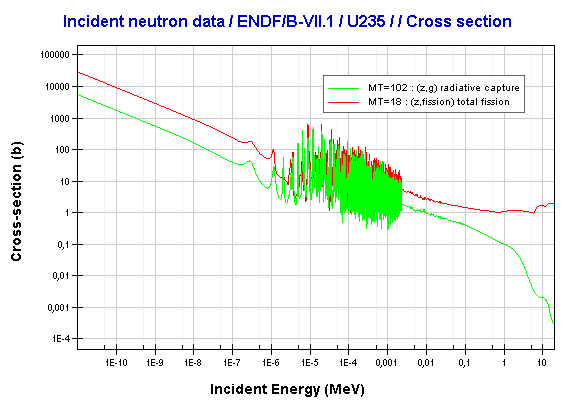
Globally, uranium-235 accounts for approximately 0.7% of naturally occurring uranium by mass, making it significantly rarer than uranium-238.
Natural uranium consists of about 99.28% U-238 and 0.72% U-235, meaning vast enrichment processes are required to boost its concentration. In power plants, enriched uranium typically reaches 3–5% U-235—sufficient to maintain criticality without excessive risk. Yet even trace enriched uranium powers satellites, research laboratories, and defense systems, underscoring its strategic value.
The need for enrichment transforms U-235 from a passive component into an active resource, tightly managed through technical and regulatory frameworks.
In civilian energy, uranium-235 has revolutionized electricity generation. Nuclear reactors fueled by enriched uranium now supply about 10% of global power, with countries like France—where nuclear generates over 70% of electricity—relying deeply on this isotope.
The efficiency of uranium-235-based fission allows reactors to operate for years on minimally enriched fuel, with modern designs pushing enrichment levels to 5%
Related Post

Does Mucinex DM Make You Sleepy? The Surprising Truth Behind This Common Cold Medication
Garcelle Beauvais Bio Wiki Age Parents Husband Children Twins The Real and Net Worth
Kathy Orr Fox 29 Bio Wiki Age Family Husband Daughter House and Net Worth

