Unveiling TV Display Technology: From LCD to MicroLED — The Evolution That’s Redefining How We Watch
Unveiling TV Display Technology: From LCD to MicroLED — The Evolution That’s Redefining How We Watch
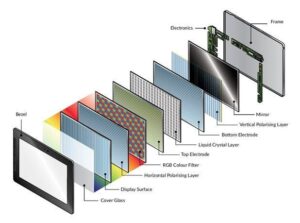
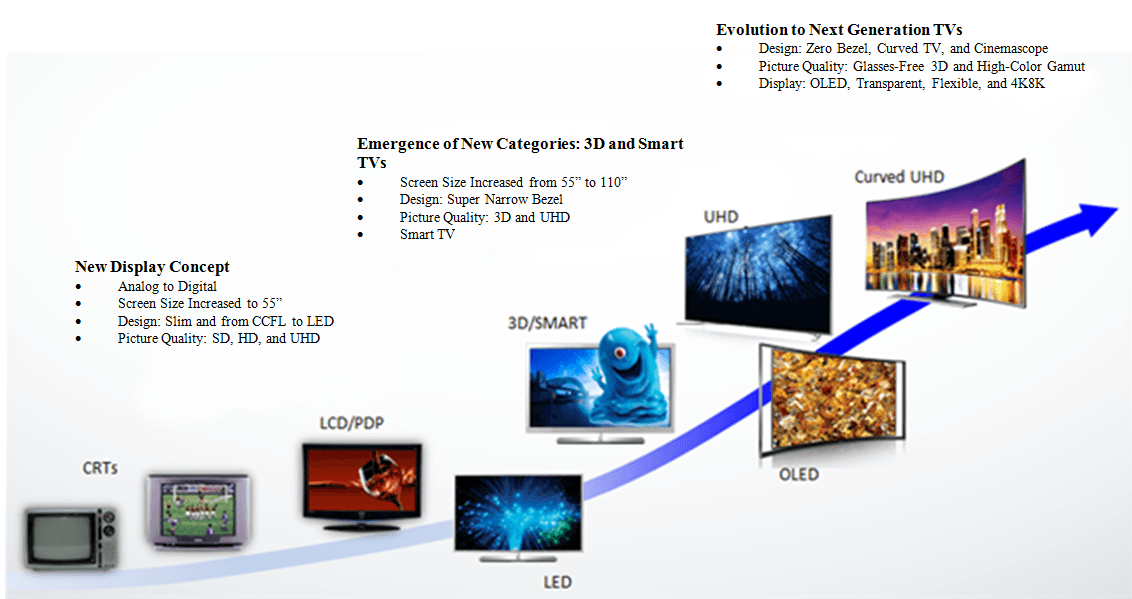
From the first bulky cathode ray tube television sets to today’s ultra-slim, vibrant OLED and emerging MicroLED panels, TV display technology has undergone a meteoric transformation. The rapid advancements in materials, engineering, and pixel architecture have revolutionized the visual experience, blurring the line between entertainment and immersive reality. Modern displays no longer just deliver images—they recreate atmospheres, render lifelike textures, and shrink physical boundaries between viewer and scene.
As consumers demand ever sharper, faster, and more dynamic visuals, understanding the underlying technologies becomes essential to making informed choices in a competitive market.
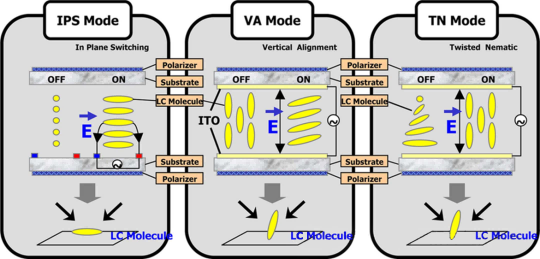
Central to this evolution is the progression of key display types, each bringing distinct advantages and limitations. Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) technology, long the industry standard, relies on liquid crystals sandwiched between polarizing layers and illuminated by bright backlights.
While cost-effective and power-efficient, LCDs struggle with true blacks and narrow viewing angles, a constraint evident when watching content from awkward angles. “LCDs offer reliability and broad compatibility,” notes Dr. Elena Moretti, display technology analyst at TechVision Labs.
“But they’re bounded by their backlight architecture, limiting contrast and color depth.”
Enter Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED), a game-changing innovation that physically emits light per pixel, eliminating backlight dependency. OLED panels deliver deep blacks—effectively zero luminance in black areas—resulting in superior contrast ratios often exceeding 1,000,000:1. The self-emissive nature also enables wider color gamuts and responsive%20response times as fast as 0.1 milliseconds, eliminating motion blur.
These attributes make OLED the preferred choice for premium home theaters and gaming setups. “OLED transforms how we perceive dynamic content—lighting every crease, shadow, and highlight with stunning authenticity,”
explains Dr. Hiroshi Tanaka, a senior engineer at LG Display.
“It’s not just better resolution; it’s a leap in visual fidelity.”
While OLED enjoys widespread acclaim, its lifespan remains a consideration, particularly for white-péd入墙alto-backlit panels at high brightness over time. Here, Mini-LED emerges as a compelling hybrid solution. Though technically built around conventional LED arrays, Mini-LED uses hundreds of smaller light sources—each with localized dimming zones far finer than standard LED backlights.
This enables dramatic contrast improvements and brightness levels rivaling OLED without organic material degradation. Consumer Electronics Show recent demonstrations have showcased Mini-LED TVs hitting over 2000 nits peak brightness, opening new doors for HDR and live sports viewing in well-lit rooms.
Beyond the dominant panel types, emerging technologies are beginning to reshape expectations.
Micro-LED, the holy grail of display innovation, promises the antithesis of LCD’s limitations: trillions of microscopic LEDs per square inch, individually controllable for perfect blacks and endless luminance. Unlike OLED, Micro-LED is not degraded by prolonged brightness, offering mill influencé lifetime exceeding 100,000 hours—virtually indestructible for future generations. While manufacturing challenges and data projection complexities keep mass adoption years away, leading brands like Samsung, TCL, and Sony are already investing heavily in scaling production.
“Micro-LED represents the cusp of a new visual era,”
states Professor Li Wei, microelectronics researcher at Tsinghua University. “This isn’t just a better screen—it’s a fundamental shift in how displays interact with light.”
Critical to effective viewing is understanding refresh rates and motion handling, especially for fast-paced content like sports or action films. Modern TVs commonly support 60Hz to 240Hz refresh rates, with adaptive sync technologies like AMD FreeSync and AMD Variable Refresh Rate minimizing screen tearing and input lag.
OLED and Micro-LED naturally excel here due to pixel-level dimming response, but even high-end LCDs now achieve 120Hz with advanced drivers. Interactive features such as 4K 120Hz for gaming, HDR10+ Dynamic Metadata, and Local Average Dimming bring real-time scene adaptation—elevating immersion beyond passive watching.
HDR (High Dynamic Range) has become a de facto standard across premium TVs, expanding color depth beyond Rec. 709 to Rec.
2020 and boosting brightness for lifelike contrast. Media consultants emphasize that TVs certified with Dolby Vision or HDR10+ deliver “cinematic color accuracy,” whether streaming Netflix originals or playing cinematic releases. “HDR isn’t just about sharper highlights,”
explains video technology journalist Mara Chen.
“It’s about preserving detail across the entire brightness spectrum, mimicking how the human eye perceives natural light.”
Form factors also influence the experience. Wall-mounted and corner-screen panels broaden viewing angles beyond traditional 16:9 limitations, while transparent and flexible OLED panels are beginning to appear in niche applications—from augmented reality interfaces to curved automotive displays. Emerging flexible and ultra-thin form factors suggest displays will soon integrate seamlessly into everyday environments, not just static flat panels.
Despite this technological surge, practical considerations remain crucial.
Cost still defines access—OLED and Micro-LED remain premium investments, while LCDs dominate the budget and mid-range segments. Power consumption, thermal management, and panel longevity influence long-term ownership value. Furthermore, calibration and color accuracy vary across models, underscoring the need for professional or precise auto-calibration tools to fully appreciate a TV’s potential.
Finally, smart integration defines modern TV evolution. Built-in Wi-Fi, voice assistants, and ecosystem compatibility with smartphones, tablets, and gaming consoles transform the unit from a static screen into a central hub of connected entertainment. Over-the-air updates and adaptive brightness ensure longevity, keeping connected devices relevant amid rapidly shifting content platforms.
In essence, TV display technology stands at the frontier of visual science—where chemistry, nanotechnology, and engineering converge. Every leap, from LCD’s reliability to OLED’s depth and Mini-LED’s brightness, brings us closer to displays that don’t just show images but simulate presence. As Micro-LED moves from prototype to pr

Related Post
Danielle Colby Bio Wiki Age Husband American Pickers and Net worth
Live Badminton Matches Today: Malaysia Match Times Revealed

Ski Shot: Mastering the Art of Precision in Snow Sports for Elite Performance

