Unveiling Pure Substance Meaning: The Essence That Defines Pure Chemicals
Unveiling Pure Substance Meaning: The Essence That Defines Pure Chemicals
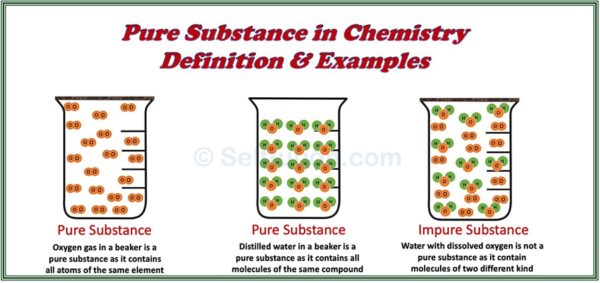
In the silent world beneath microscopes and lab benches, pure substances stand as the foundational pillars of chemistry—unambiguous, immutable, and utterly defined. Unlike mixtures, which blend elements without altering their intrinsic nature, pure substances maintain consistent composition and identical properties across every sample. From water (H₂O) to sodium chloride (NaCl), these chemical entities represent nature’s most precise building blocks.
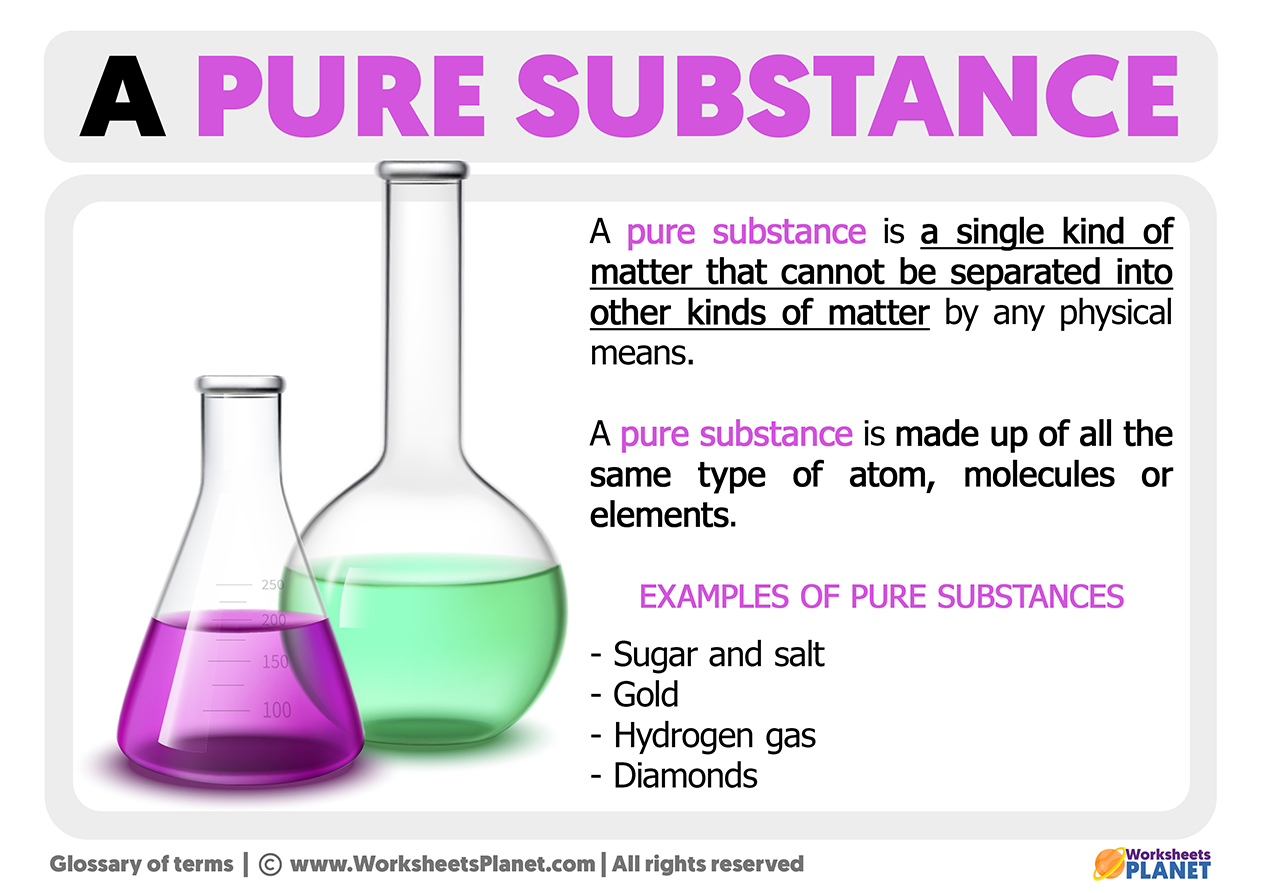
Understanding pure substance meaning is not merely academic—it is the gateway to unlocking breakthroughs in medicine, materials science, environmental analysis, and beyond. At the heart of pure substance meaning lies definition: a material with a fixed chemical formula, uniform molecular structure, and predictable physical and chemical behavior. “A pure substance is a single type of matter with a constant composition,” explains chemist Dr.
Elena Torres of the Institute of Advanced Chemistry. “Unlike mixtures, where components can vary, each molecule of pure substance is identical in mass and properties.” This consistency enables scientists to rely on pure substances for accurate experimentation, pharmaceutical development, and industrial precision. ### The Core Characteristics of Pure Substances Pure substances are distinguished by four defining traits: - **Uniform Composition**: Every sample shares the same chemical makeup.
A vial of pure ethanol, for example, delivers exactly C₂H₅OH at molecular level. - **Constant Physical Properties**: Melting points, boiling temperatures, and density remain invariant—critical for quality control in manufacturing. - **Indivisibility at Molecular Level**: While compounds can be broken into simpler molecules, the fundamental structure remains unaltered, preserving the substance’s identity.
- **Reproducibility**: Purity ensures that chemical reactions proceed predictably, enabling scalable and reliable results.
Types of Pure Substances: Elements and Compounds
Pure substances fall into two classes: elements and compounds, each carrying distinct meanings within chemistry. - **Elements** are pure substances composed of only one atomic species, symbolized by their atomic number.Oxygen, iron, and gold exist naturally or synthetically as single-element forms. “Elements are the ultimate units of chemical identity,” notes Dr. Torres.
“Water isn’t an element—it’s a compound, but each element exists inherently pure.” - **Compounds** emerge when two or more elements chemically bond in fixed ratios. Sodium chloride (NaCl) is a perfect example—gold and sulfur do not form a compound under normal conditions, but sodium and chlorine do, yielding a stable, predictable material. Some compounds exist in multiple crystalline forms, called polymorphs, which may differ slightly in molecular arrangement but retain identical composition—a subtlety vital in pharmaceutical development where bioavailability can hinge on crystal structure.
Purity Assessment: The Science Behind Definition
To confirm a substance’s purity, scientists rely on precise analytical methods rooted in physical and molecular diagnostics. These include: - **Mass Spectrometry**: Identifies molecular weight and elemental composition with atomic-level precision. - **Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)**: Reveals molecular structure by detecting nuclear spin in magnetic fields.- **Infrared Spectroscopy**: Maps molecular bonds through vibrational resonance patterns. - **Elemental Analysis**: Quantifies constituent atoms via combustion or mass separation techniques. “Accuracy in purity testing is non-negotiable,” Dr.
Torres emphasizes. “Even trace contaminants—measured in parts per million—can drastically alter a substance’s reactivity, especially in life-saving drugs.” Modern labs enforce rigorous protocols to minimize impurities, ensuring that substances labeled as ‘pure’ meet exacting industry and regulatory standards.
In pharmaceuticals, the meaning of pure substance translates directly to human impact: every tablet, injectable, or topical formulation depends on chemically pristine ingredients.
For example, aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) must be synthesized without impurities to prevent adverse reactions or diminished therapeutic effect. Similarly, in semiconductor manufacturing, ultra-pure silicon forms the bedrock of microchips, where even atomic-scale contamination disrupts conductivity.
Beyond the Lab: Applications and Real-World Implications
The meaning of pure substances extends far beyond controlled laboratory settings, shaping industries and daily life. In environmental science, pure reference materials calibrate instruments measuring pollutants, ensuring accurate data for climate and air quality monitoring.In food technology, pure sugars and emulsifiers deliver consistent flavor, texture, and shelf life. Forensic science leverages pure substance analysis to detect trace evidence—paint particles, fibers, or toxins—with near-scientific precision. Materials innovation also advances through deliberate purity engineering: - High-purity germanium is essential in infrared optics and quantum sensors.
- Supercritical carbon dioxide, a ‘pure’ fluid state, revolutionizes green extraction processes in pharmaceuticals and flavors. - In nanotechnology, pureness prevents unwanted clustering, preserving the intended functionality of engineered nanoparticles.
Yet the concept of purity is evolving.
As chemists probe deeper into nanostructures and quantum materials, the boundary between ‘pure’ and ‘imperfect’ blurs—atomic defects or dopants now intentionally engineered to tune properties. This refinement underscores a broader truth: while pure substance meaning remains rooted in consistency and invariance, application and interpretation continue to expand the frontier.
Ultimately, pure substance meaning is the cornerstone of chemical identity—where definition meets function, and purity becomes power. From the smallest molecule to industrial-scale production, these substances are more than matter: they are the language of matter’s most essential truths.


Related Post

Gore El Patron: The Unforgettable Gangster Who Redefined Fear in the Underground
What we know about Cara Whitney the wife of legendary American comedian Larry the Cable Guy
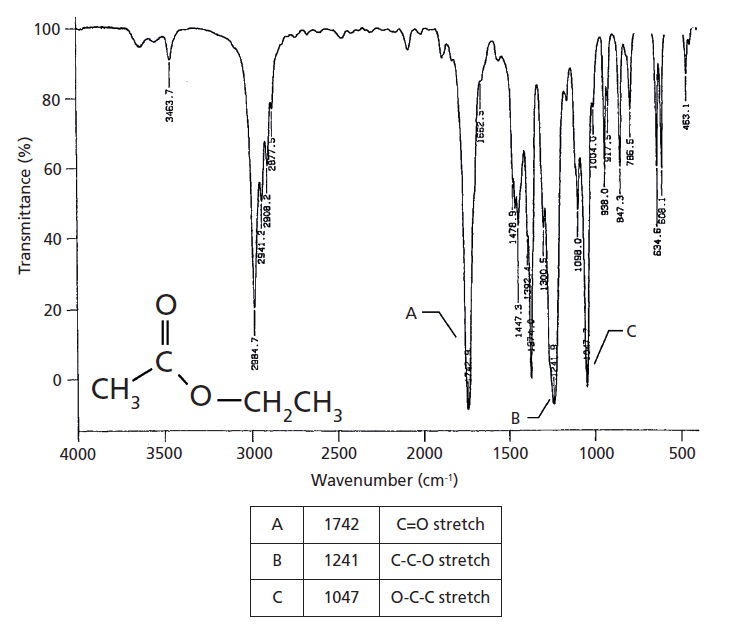
Unlocking Matter: The Far-Reaching Influence of the Ir Spectrum of Ether in Science and Beyond

The Ultimate Rumble: Pacquiao vs Mayweather — Who Truly Dominated the Ring?

