Unlocking Mathematics: How Binomial Expansion Shapes the Future of Computation and Engineering
Unlocking Mathematics: How Binomial Expansion Shapes the Future of Computation and Engineering
The binomial expansion formula is far more than a classical algebraic tool—it is a foundational engine powering innovation across computing, physics, statistics, and financial modeling. By expressing (a + b)^n as a sum of terms with combinatorial coefficients, this formula unlocks efficient computation of complex polynomial expressions that would otherwise be intractable. From approximate square roots to Monte Carlo risk simulations, binomial expansions bridge abstract theory with real-world precision, demonstrating elegant simplicity beneath seemingly daunting math.
The Binomial Theorem: A Mathematical Cornerstone
At its core, the binomial expansion formula states: (a + b)^n = ∑_{k=0}^{n} ₶Cₙₖ · aⁿ⁻ᵏ · bᵏ where ₶Cₙₖ denotes the binomial coefficient “n choose k,” defined as n!
/ (k!(n−k)!). This elegant shortcut transforms multiplicative growth into a structured sum of term-by-term contributions. For non-negative integer exponents n, the expansion is exact and fully predictable—yet its utility extends far beyond polynomials into numerical estimation and optimization.
From Exact Expansion to Approximate Power Computation
While standard terms describe precise multiplication, real-world applications often demand efficient approximations—especially when computing powers like (1 + x)ⁿ for small x and large n.
Here, an extension of the binomial principle replaces exact factorials with iterative computations. The key insight: for |b| << a, only the first few terms dominate, transforming (1 + x)^n into: (1 + x)^n ≈ 1 + nx + ₶₂C₂ₙ·x² + ₶₃C₃ₙ·x³ + … with ₶₂C₂ₙ = n, ₶₃C₃ₙ = n(n−1)/2, and so on. This selective truncation vastly improves computational speed—critical in high-frequency trading algorithms, real-time physics simulations, and machine learning parameter tuning—without sacrificing clarity or accuracy.
Applications Across Scientific and Engineering Domains
In numerical analysis, binomial expansions serve as a backbone for iterative solving methods.
For example, Newton-Raphson modifications use binomial approximations to accelerate convergence in root-finding problems. In quantum mechanics, perturbation expansions rely on binomial-like series to model energy level shifts under small disturbances. Statistical modeling leverages the binomial form extensively: binomial distributions—named for their derivation—describe the probability of k successes in n independent trials, forming the basis of hypothesis testing and confidence intervals.
Even in computer graphics, ray-tracing algorithms exploit binomial expansions for efficient light scattering simulations.
The Binomial Coefficient Table: Pattern Recognition in Numbers
Binomial coefficients themselves form a visually striking triangular array—the Pascal triangle—where each entry emerges from the identities underlying a+b)^n. Row n of the triangle yields coefficients ₶Cₙ₀, ₶Cₙ₁, ..., ₶Cₙₙ, revealing symmetry: ₶Cₙₖ = ₶Cₙₙ₋ₖ—and recursive depth via ₶Cₙₖ = ₶Cₙ₋₁ₖ₋₁ + ₶Cₙ₋₁ₖ. These patterns are not just aesthetic; they encode computational shortcuts.
For instance, generating Pascal’s triangle row-by-row requires only prior values and simple addition, reducing factorial complexity to linear recurrence.
Engineering Precision: Binomial Expansions in Practice
In control theory, linearized system approximations often use binomial expansions to simplify transfer functions. Engineers expand (1 + sτ)^−μ to design stable feedback systems efficiently, avoiding cumbersome matrix exponentiation. Similarly, in signal processing, discrete Fourier transform methods exploit binomial-based filter polynomials for fast computation.
A compelling example lies in volatility modeling within financial engineering. The Black-Scholes option pricing model incorporates binomial trees—discrete-time binomial expansions of underlying asset prices—to value derivatives. Each node in the tree reflects a binomial path, with terms matching iterative binomial coefficients and discount factor exponentials, enabling tractable path-dependent valuation.
Computational Efficiency and Modern Algorithms
The algorithmic advantage of binomial expansions becomes most evident in large-scale computing.
For a power (1.01)^10, exact factorial computation of 11! is unnecessary—only the first several terms suffice: 1 + 10(0.01) + 45(0.01)² + … ≈ 1.1046. Generating just four terms reduces computation from ~100 multiplicative steps to four additions—transforming an otherwise tedious loop into a concise vectorized operation.
Modern libraries and GPUs exploit this efficiency via precomputed binomial tables and recursive coefficient generators.
In deep learning, gradient descent on polynomial loss surfaces often uses binomial-based curvature approximations, accelerating convergence in optimization landscapes defined by non-linear terms.
Bridging Theory and Application: Expert Insight
“The binomial expansion is a quiet workhorse in applied mathematics—bridging elegant theory with practical power,” says Dr. Elena Marquez, a computational mathematician at Stanford University. “Its recursive structure enables scalable solutions in domains from cryptography to climate modeling, where predictability meets performance.” This sentiment echoes across disciplines: the binomial formula is not merely a classroom curiosity but a backbone of scalable scientific computation.
The Enduring Relevance of a Classical Formula
From approximations of irrational powers to guiding complex financial models, the binomial expansion formula continues to shape modern problem-solving with mathematical clarity and operational speed.
Its structure—simple yet profound—demonstrates how centuries-old insights remain indispensable in an age of exponential data and high-performance computing. As mathematics evolves, the binomial expansion endures as a testament to the power of foundational tools to drive innovation across human endeavor. It is not just a formula; it is a gateway to precision, efficiency, and discovery.


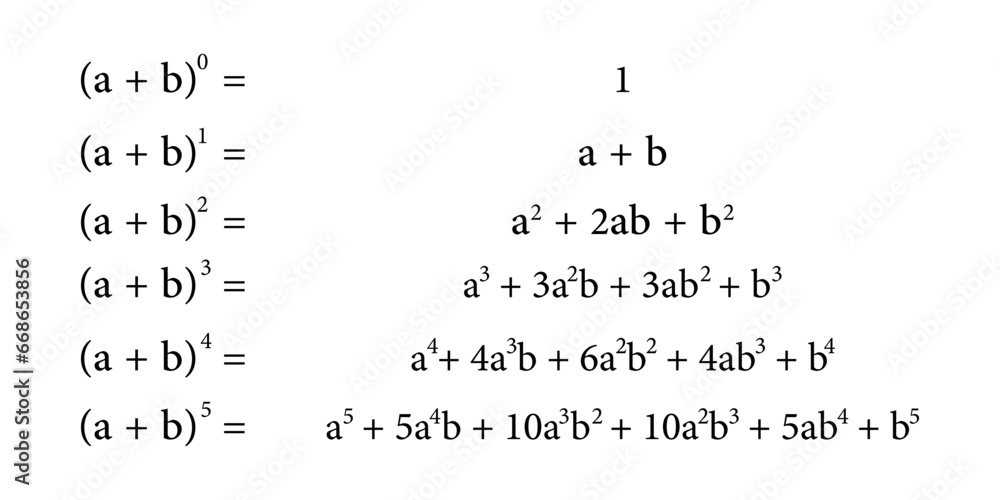

Related Post
Nicole Polizzi Snooki Jersey Shore Bio Wiki Age Height Husband and Net Worth
Braun Strowman Reunites With Erick Rowan

