Unlocking Investment Potential: The Critical Role of Undepreciated Capital Cost in Modern Financial Analysis
Unlocking Investment Potential: The Critical Role of Undepreciated Capital Cost in Modern Financial Analysis
Investors and developers constantly seek reliable metrics to evaluate long-term profitability—nowhere is this more vital than in the assessment of capital investments where depreciation truly matters. At the heart of accurate financial forecasting lies undepreciated capital cost, a foundational yet often overlooked expense category that reflects the actual replacement or maintenance costs of physical assets not subject to depreciation in accounting terms. Unlike accelerated or book depreciation, this undepreciated amount captures real-world replacement needs, offering a clearer picture of sustainable costs and enabling more precise return on investment calculations.
Understanding and correctly applying undepreciated capital cost transforms how organizations plan projects, allocate capital, and measure long-term value creation.
Understanding Undepreciated Capital Cost: Definition and Practical Meaning
Undepreciated capital cost refers to the perpetual cost required to restore a capital asset to its original functional condition, excluding accounting depreciation. It represents the minimum investment needed to maintain operational efficiency without incurring losses from outdated or damaged infrastructure.While depreciation reduces book value over time—often misconstrued as a proxy for cost—real-world scenarios demand funds precisely outside that减值. For example, a manufacturing plant’s $10 million machinery may have undergone 30% depreciation on paper, but its undepreciated cost could remain $7 million—reflecting the expense required to replace or upgrade components that degrade beyond accounting entries. This distinction is crucial: undepreciated cost is not an accounting line item but a forward-looking operational threshold.
How Undepreciated Capital Cost Shapes Investment Decisions
Undepreciated capital cost serves as a linchpin in capital budgeting, influence investment appraisals, and recalibrates risk assessments.Traditional metrics like Net Present Value (NPV) and Internal Rate of Return (IRR) depend heavily on accurate cost inputs—errors here distort projections and mislead decision-makers. By isolating genuine expansion or replacement needs, analysts avoid underestimating true infringement costs. For instance, a utility company planning grid upgrades must account not only for asset inflation but also for the undepreciated cost of replacing transformer stations worn by external wear, not just accelerated depreciation schedules.
As one senior infrastructure planner noted, “Treating depreciation as a cost shield blinds us to real-world obsolescence. Undepreciated capital cost reveals hidden balance sheet vulnerabilities that can make or break a billion-dollar project.”
Applications Across Industries: Real-World Use Cases
In practice, undepreciated capital cost manifests across diverse sectors where long-lived assets drive competitive advantage. - **Energy Infrastructure**: Utility firms apply the metric to plan perpetual replacements of pipelines, substations, and generators beyond book value.-
Utilities and Grid Maintenance
Utilities routinely calculate undepreciated replacement costs to align capital expenditure (CAPEX) with asset life cycles. For example, replacing aging transformers—whose functional life often remains intact despite accounting gains—ensures grid reliability without budget shortfalls. Energy analysts stress that ignoring undepreciated costs results in deferred maintenance and higher long-term risks.-
Manufacturing and Industrial Assets
Factories upgrading machinery factor in undepreciated costs when evaluating throughput improvements. Installing a high-efficiency CNC machine may carry substantial upfront replacement value beyond its depreciated book value, directly affecting ROI and go/no-go decisions. -Real Estate Development and Commercial Property
Commercial developers use undepreciated capital cost to initiate phased renovations in aging buildings.Rather than deferring costly façade, roofing, and MEP system upgrades based on assetbook declines, players reinvest proactively, preserving asset value and tenant satisfaction. -
Transportation and Public Works
Transit agencies rely on undepreciated cost projections to maintain rail tracks, signaling systems, and fleet vehicles. Routine upgrades prevent cascading failures and optimize lifecycle cost efficiency, especially as fleets age beyond traditional depreciation timelines.Integrating Undepreciated Cost into Financial Models: Standards and Challenges
Incorporating undepreciated capital cost into financial planning requires disciplined methodology. Unlike depreciation, which follows statutory schedules, undepreciated cost is project-specific and often estimates based on market replacement rates, labor trends, and materials inflation. Financial professionals employ several key strategies: - Historical data comparison: Analysts benchmark component-level replacement costs against regional indices and construction cost reports.- Expert consultation: Engaging engineers and site managers improves accuracy by grounding assumptions in physical wear patterns and operational stressors. - Scenario modeling: Sensitivity analysis tests how variations in material costs or labor availability shift undepreciated figures, preparing organizations for volatility. - Portfolio-level aggregation: Consolidating undepreciated costs across asset classes ensures comprehensive visibility and avoids underestimation from siloed assessments.
While the process demands rigor, the payoff is decisive: investments grounded in real replacement economics deliver higher, more sustainable returns than those built on accounting heuristics alone.
Policy Implications: Aligning Public and Private Capital Planning
Governments and public institutions increasingly recognize undepreciated capital cost as essential to fiscal transparency and long-term service delivery. Public infrastructure programs, for example, benefit from explicit undepreciated cost allocations to justify funding requests and prioritize projects with true lifecycle value.Transparent reporting enhances accountability, prevents budget shortfalls, and strengthens public trust. As a policy analyst emphasized, “When citizens see tax dollars directed toward real replacement needs—not swept depreciation lines—the credibility of infrastructure investment soars.” Moreover, regulatory frameworks promoting undepreciated cost visibility support better risk management across sectors, curbing costly surprises and fostering resilience in national and municipal balance sheets.
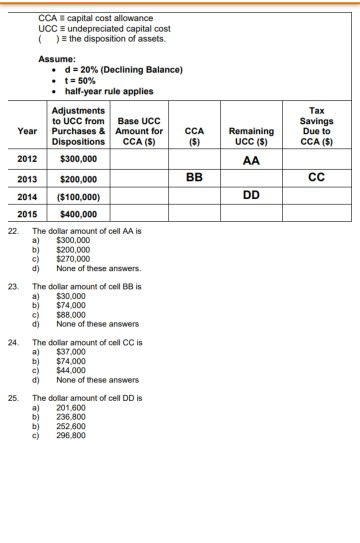
Expert Insights: Why Undepreciated Capital Cost Is Non-Negotiable
Industry leaders stress undepreciated capital cost as more than an accounting nuance—it’s a strategic imperative. A senior infrastructure finance officer observes: “Depreciation masks obsolescence.If we ignore what it truly costs to maintain functionality, we design unbankable projects from day one.” This perspective underscores a broader shift toward asset-based financial reasoning. Investment committees now demand detailed undepreciated cost breakdowns alongside cash flow projections, treating them as critical inputs that separate sustainable ventures from financially fragile ones. In an era of climate uncertainty and aging infrastructure globally, this focus on realistic capital sizing ensures resources are deployed where they deliver lasting value, not just near-term accounting gains.
Looking Ahead: The Evolving Landscape of Capital Cost Assessment
As digital tools and data analytics mature, estimation of undepreciated capital cost becomes increasingly dynamic and precise.Advanced modeling platforms integrate real-time supply chain data, predictive maintenance algorithms, and AI-driven failure forecasting—tools that sharpen away guesswork. The integration of digital twins in asset management, for instance, enables simulations of degradation patterns, automating undepreciated cost calculations with unprecedented accuracy. This technological evolution fortifies capital planning, making once-subjective figures data-driven and auditable.
Looking forward, the convergence of financial discipline, asset intelligence, and real-time analytics positions undepreciated capital cost as a cornerstone of resilient, future-ready investment strategies. For every dollar guided by realistic replacement needs, organizations strengthen their foundation—ensuring longevity, investor confidence, and enduring competitiveness in an ever-changing global marketplace.

Related Post

Undepreciated Capital Cost: The Hidden Engine Driving True Investment Value

What Is Undepreciated Capital Cost? Unlocking Its Role in Accounting and Asset Valuation

How Candace Owens’ Children’s Names Reflect a Legacy of Identity, Strength, and Cultural Balance

Marisa Maez: Pioneering the Future of Data-Driven Storytelling in Digital Media

