The R22 Pressure-Temperature Chart: Decoding Refrigerant Behavior Under Pressure
The R22 Pressure-Temperature Chart: Decoding Refrigerant Behavior Under Pressure
Understanding the behavior of refrigerants under varying pressure and temperature conditions is essential in HVAC and industrial refrigeration systems—but few tools illustrate this complexity with greater precision than the R22 Pressure-Temperature chart. This deceptively simple diagram reveals the intricate thermodynamic relationships that govern R22, a chlorodifluoromethane once widely used as a refrigerant before being phased out due to environmental concerns. While R22 is no longer industrially produced, its pressure-temperature profile remains a cornerstone for troubleshooting, maintenance, and safe handling of legacy systems still in operation.
At the heart of refrigeration physics lies the intimate relationship between pressure and temperature: as pressure increases, so does vapor temperature, and vice versa—yet not in a linear fashion. The R22 Pressure-Temperature chart visualizes this non-linear dance, charting critical points such as saturation curves, critical temperature (the point above which liquid and vapor cannot coexist), and condensation zones. These data points determine safe operating limits, enabling technicians to detect anomalies like subcooling, superheating, or improper phase changes before they trigger system failure.
Key Features of the R22 Pressure-Temperature Chart
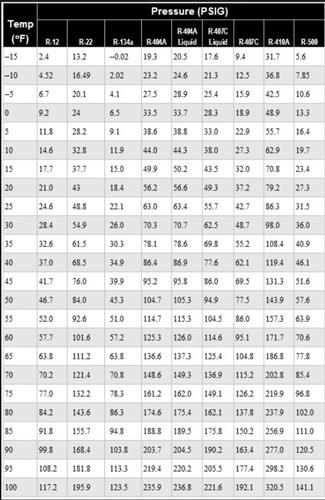
The chart maps R22 across a defined range of pressures, typically from 0 to approximately 25 bar (gauge pressure), and plots corresponding temperature values at saturation (liquid-vapor equilibrium).Key regions to understand include: - **Low-Pressure Zone (Low-Temperature Range, ~−40°C to 10°C):** At pressures around 0–5 bar, R22 liquefies at near-liquid temperatures. This range is critical in evaporator coils and low-temperature applications. - **Normal Operating Range (~5 to 15 bar):** Within 5–15 bar, R22 operates in a two-phase state, ideal for most HVAC systems.
Minimal superheat (typically 5–10°C above saturation temperature) ensures efficient heat rejection. - **High-Pressure Zone (15–25 bar):** Elevated pressures push the state closer to critical conditions (~−15°C critical temperature), where vapor and liquid properties blur. Operating here risks compressor damage due to un expansion or flooding.
One of the chart’s most valuable insights is identifying phase boundaries: where R22 transitions between saturated liquid, saturated vapor, and superheated vapor. These phase changes define the refrigeration cycle’s efficiency—any deviation can impair system performance. For instance, “wet” combustion (too much liquid) in compressors causes catastrophic failure, a risk the chart helps mitigate through accurate pressure monitoring.
Critical Operating Points and Safe System Limits
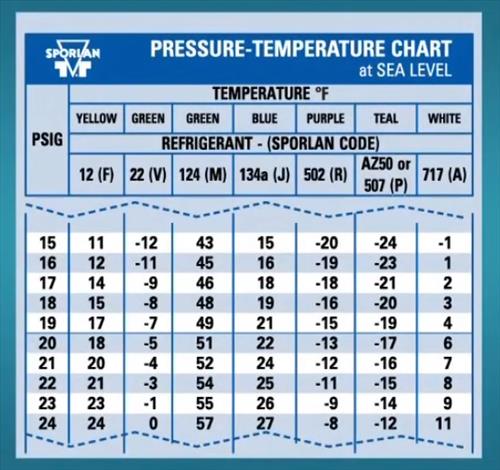
The R22 chart highlights pivotal operational thresholds every technician must remember.The saturation curve defines the temperature at which R22 fully vaporizes or condenses at a given pressure. For example: - At 10 bar (gauge), R22 boils near **−20°C**. - At 20 bar, saturation temperature plummets to approximately **−50°C**.
- Above 25 bar, nonlinearities intensify, approaching the critical point (~−15°C), where phase distinction dissolves. Monitoring pressure deviations beyond these limits can cause system stress: high pressure increases compression work, raising energy consumption; low pressure risks liquid slugging, which floods compressors. The chart’s slope—steeper at lower pressures—emphasizes heightened sensitivity in cold environments.
“A 1 bar error in pressure measurement at ambient conditions can shift the rational operating window by tens of degrees,” warns systems engineer Dr. Lena Torres, noting that even minor deviations risk reduced efficiency or component fatigue over time.
Equally vital are the “trip points” plotted indirectly through temperature thresholds: exceeding saturation temperature leads to excessive superheat, while sustained subcooling exceeds design capacity.
Proper system charging ensures pressure stays within the yellow “sweet spot” defined by manufacturer specs, visually delineated on the chart’s safe zone.
Practical Applications in Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Technicians rely on the R22 Pressure-Temperature chart daily for precise diagnostics. During routine servicing, pressure readings at evaporator or condenser ports yield temperature estimates—matching these to the chart reveals phase conditions. For instance, detecting 30°C at 12 bar signals saturated vapor (superheat might be 20°C), prompting flush checks for moisture contamination.Similarly, reading 45°C at the same pressure indicates subcooling, suggesting possible pressure drops or coil fouling.
“The chart isn’t just a static diagram—it’s a diagnostic compass,” explains HVAC consultant Marcus Reid. “Every deviation from the expected curve tells a story: a refrigerant short, a leak, or a faulty sensor.
Diagnose with the chart, act before failure.”
Environmental and Safety Implications
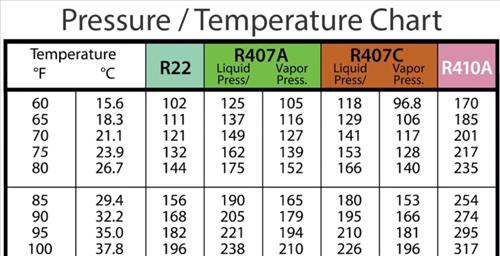
Though R22’s use is banned under the Montreal Protocol due to its high Global Warming Potential (GWP), systems serviced with original R22 still exist across commercial and industrial sectors. The Pressure-Temperature chart remains indispensable in such contexts: mischarging R22—even slightly—alters thermodynamic balance, increasing leak risks and environmental release. Ensuring precise pressure control minimizes emissions and maintains retrofit compatibility.Quotation: “The chart bridges past and present,” notes icebergs and HVAC specialists — “while we no longer produce R22, understanding its fundamental behavior ensures safer, greener operations today.”
The R22 Pressure-Temperature chart, though rooted in a discontinued refrigerant, endures as a vital educational and operational tool. It encapsulates the delicate balance of phase change mechanics that underpin refrigeration, empowering technicians to maintain system integrity, optimize efficiency, and prevent costly failures—proof that foundational scientific insight remains impactful long after its commercial life ends.

Related Post

Unveiling São Paulo's Challenging Neighborhoods: A Candid Look at Urban Margins

The Unseen Roots Behind Jericka Duncan’s Rise: Exploring Her Parents, Family, and Early Influences
Juju Chang ABC Age Height Sister Family Husband Sons Salary Net Worth
Megan Fox Erome Unveiling The Enigmatic Allure

