Pressure Gradient Force: The Force Behind Every Wind, Every Storm
Pressure Gradient Force: The Force Behind Every Wind, Every Storm
At the heart of every atmospheric movement lies an invisible but relentless driver: the pressure gradient force. This fundamental physical mechanism governs air motion across the globe, shaping winds, driving weather systems, and even influencing climate patterns. Without understanding this force, predicting storm paths or explaining daily breezes remains impossible.
From calm mornings to violent hurricanes, the pressure gradient force acts as nature’s subtle conductor, orchestrating the flow of air with precision and power.
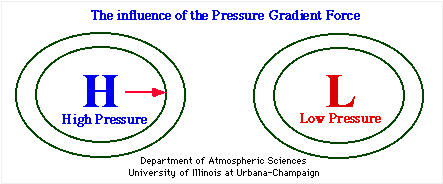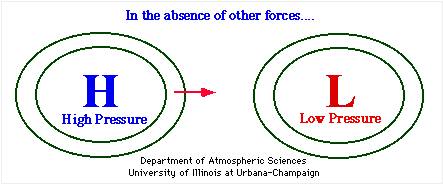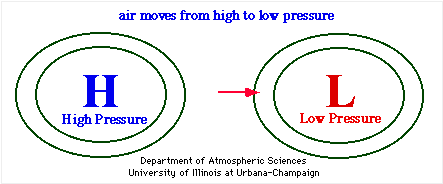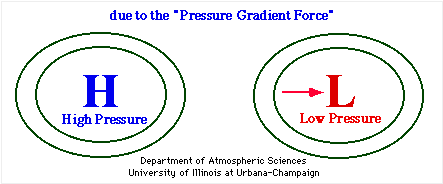
At its essence, the pressure gradient force arises from differences in atmospheric pressure across a given distance. Air naturally flows from regions of high pressure to low pressure, seeking equilibrium.
This movement is not merely random but driven by a precise physical incentive—pressure imbalance. “The basic economics of atmospheric motion is simple: air moves from high to low pressure,” explains meteorologist Dr. Elena Ruiz.
“The steeper the pressure difference, the stronger the resulting force—and the faster the wind.” Quantifying this, the force per unit mass is proportional to the pressure gradient, making even tiny pressure changes significant over large distances.
The Physics Behind the Push: Understanding Pressure Gradient Force
The pressure gradient force is defined mathematically as the difference in pressure over space, pushing air from high-pressure zones to low-pressure zones. Its magnitude depends on two key factors: the magnitude of the pressure difference and the spatial scale—namely, the distance over which that difference occurs.A narrow pressure difference over a short distance generates a strong, localized force; in contrast, a broad gradient spreads the same pressure change across kilometers, reducing peak wind intensity but enabling large-scale weather systems. Mathematically, the force intensity varies inversely with distance between pressure points. In meteorological terms, along a straight line with constant pressure, wind speed increases as pressure falls, reaching peak magnitude at the isobars—the imaginary lines connecting points of equal pressure.
This principle underpins wind prediction models used worldwide. Advanced numerical weather prediction (NWP) systems calculate pressure gradients across grids spanning hundreds of kilometers, translating them into forecasted wind speeds and storm trajectories with remarkable accuracy.
From Local Breezes to Global Currents
The pressure gradient force operates across all scales—from garden breezes to planetary wind belts.At the microscale, tiny differences between sun-exposed and shaded surfaces create local gradients, fueling morning sea breezes or valley winds. These phenomena arise because land heats faster than water, lowering pressure inland and drawing cooler air from the coast. On regional scales, pressure gradients drive daily cycles like land-sea breezes, which influence coastal climates and navigation.
More profoundly, planetary-scale pressure differences power the jet streams—fast-flowing air currents in the upper troposphere. “Jet streams are nature’s fastest winds, sustained by continental-scale pressure gradients between polar and tropical air masses,” says atmospheric scientist Dr. Raj Patel.
These narrow bands of high-speed flow steer weather systems across continents and dictate the paths of storms, impacting everything from snowfall to drought patterns.
Pressure Gradient Force and Severe Weather
When pressure gradients intensify—often along frontal boundaries where warm and cold air masses collide—wind speeds accelerate dramatically. These sharp gradients fuel some of the most destructive weather events.Tropical cyclones, for instance, form and strengthen along steep pressure gradients surrounding low-pressure centers. “A tighter pressure drop means a stronger gradient force,” explains hurricane researcher Dr. Lisa Chen.
“This translates to more intense winds, larger storm surges, and greater potential damage.” Supercell thunderstorms derive strength from localized pressure gradients within their mesocyclones, where rapid vertical motion amplifies the horizontal pressure imbalance. The result: devastating tornadoes, hail, and derechos. Even extratropical cyclones—massive low-pressure systems spanning hundreds of kilometers—gain ferocity from their expansive yet potent gradients.
Forecasters rely on precise gradient measurements to issue timely warnings, saving lives and mitigating risk.
Unveiling the Invisible: Tools and Technologies
Modern meteorology harnesses sophisticated tools to map and analyze pressure gradients in real time. Surface weather stations record pressure at fixed points; ascending balloons and aircraft collect vertical profiles; satellites detect pressure-related patterns via temperature and moisture gradients.Numerical models assimilate these data, computing pressure differences across grids to simulate future conditions. Wind profilers and Doppler radar detect subtle pressure-driven shifts in wind speed and direction, vital for aviation safety and severe storm tracking. The integration of these technologies enables forecasters to pinpoint sudden pressure shifts—key indicators of rapidly developing weather threats.
As instrumentation improves, so does our ability to predict the impacts of compression and rarefaction with greater confidence.
The Invisible Force That Shapes Our Lives
From the gentle caress of a sea breeze to the violent fury of a hurricane, pressure gradient force remains silent yet undeniably powerful. It is the invisible architect of wind, the silent driver of weather systems, and the silent force behind climate dynamics.Understanding this fundamental pressure imbalance not only illuminates current atmospheric behavior but also enhances preparedness for future extremes. As global climate shifts alter pressure patterns worldwide, the study of pressure gradients grows ever more critical. This force, though imperceptible to the naked eye, governs the rhythm of our skies and the pulse of our planet.


Related Post

The Light Within the Chest: Decoding GuideYourReflectionIntoTheLight Warframe Chest
Dakota Kai Accepts Ms WarGames As Her New Nickname
Exploring Roblox R34: What Lies Beneath the Infamy in the Subculture of Mature Gaming Content

