Pa Vehicle Registration Renewal: Your Essential Guide to Staying Compliant and Avoiding Penalties
Pa Vehicle Registration Renewal: Your Essential Guide to Staying Compliant and Avoiding Penalties
In the ever-evolving world of vehicle ownership, timely registration renewal remains a critical responsibility that ensures legal operation, financial accountability, and road safety. Every registered vehicle must remain current through seamless renewal processes, but the mechanics, frequency, and common pitfalls vary significantly depending on jurisdiction and vehicle type—making Pa Vehicle Registration Renewal a focal point for drivers, fleet operators, and policymakers alike. Mastering this process not only prevents fines and license suspensions but also supports sustainable transportation ecosystems by keeping records accurate and enforcement effective.
Vehicle registration renewal is the formal procedure through which drivers revalidate their vehicle’s legal status with local transportation authorities. This typically involves verifying ownership, providing updated insurance, paying renewal fees, and, in many cases, completing mandatory safety inspections. The timeline for renewal differs widely: while some regions renew registrations annually, others align renewals with vehicle inspection cycles every two to four years—often coinciding with state-mandated roadworthiness checks.
For example, in many U.S. states, motor vehicles must be registered every 12 or 36 months, requiring drivers to renew through state motor vehicle departments (DMVs) or online portals. In contrast, countries like Germany and Australia operate near-simultaneous renewal periods tied to annual driving permit validity, streamlining administrative burden but demanding strict adherence to calendar or inspection windows.
Failing to renew vehicle registration on time can trigger a cascade of consequences. Most notably, unregistered vehicles risk immediate impoundment by law enforcement within 30 to 90 days of expiration—depending on location. Beyond physical seizure, financial penalties compound: fines typically range from $50 to $500 per violation, with repeated lapses increasing penalties significantly.
Insurance coverage often lapses with registration, leaving drivers vulnerable to liability and legal exposure. For commercial fleets, non-compliance jeopardizes operating licenses and invites audits that expose hidden operational risks. As transportation expert Dr.
Elena Marquez notes, “Registration isn’t just paperwork—it’s evidence of due diligence. Missing renewal turns a routine responsibility into a costly liability.”
Who Must Renew and How Small Differences Shape Compliance
The obligation to renew vehicle registration applies broadly, but nuances in vehicle classification, ownership status, and residency status determine the exact procedure. Private driver’s licenses generally require renewal every 2 to 4 years, with fees ranging from $10 to $100, depending on the state and vehicle value.Commercial operators, including commercial trucking companies and ride-share platforms, face more complex requirements: annual renewals are mandatory, often linked to commercial vehicle permits, and may demand additional documentation such as proof of fleet registration, insurance liability coverage, and audited annual safety reports.
Residents and non-residents experience distinct renewal pathways. In U.S.
states like California, residency-based rules mean out-of-state drivers must register with a local DMV and submit temporary cards until permanent status is confirmed. Non-residents may renew temporarily but face stricter penalties if operating in the state beyond their allowed period. Similarly, countries like Canada enforce provincial registration systems—Ontario, for instance, allows border-crossing drivers to renew via mail or online, but obstructive delays can lead to warrantless roadside detentions.
Geographic variation further complicates renewal timelines. Remote or rural areas may impose longer processing periods due to limited office access, while urban centers often offer expedited online renewals within 24–48 hours. Technological adoption—such as digital portals, mobile apps, and automated payment systems—has significantly reduced administrative delays, particularly in countries investing in integrated transport databases.
Yet, rural or low-connectivity zones still face bottlenecks, requiring proactive use of public service offices or mobile units.
Fees, Documents, and the Renewal Checklist: Preparing for Smooth Processing
Vehicle registration renewal fees are generally standardized but influenced by vehicle type, age, and local policy. In Texas, for example, the base renewal fee is $30–$70, while electric or specialty vehicles often incur surcharges.Emerging trends show some municipalities adopting dynamic pricing—lowering fees for low-emission vehicles to encourage green adoption—while others leverage usage-based models, adjusting costs according to annual mileage or commercial activity.
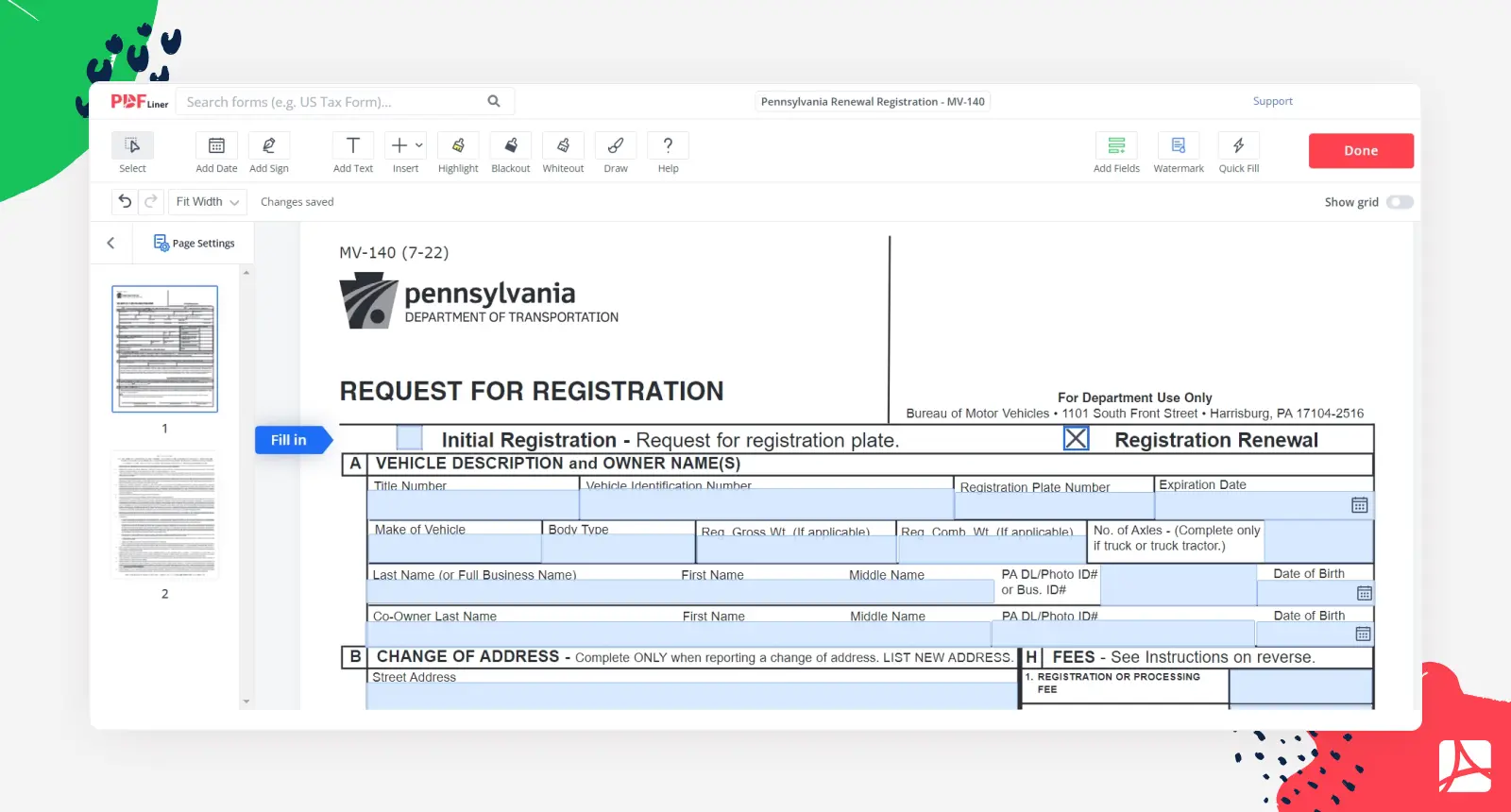
A comprehensive renewal checklist ensures nothing is overlooked: - Verify vehicle identification number (VIN), make, model, and year match DMV records. - Confirm ownership through title documents, issuing authority, and proof of insurable interest.
- Provide current, valid insurance records—minimum liability coverage is standard. - Collect player-style identification (driver’s license or commercial operator ID). - Schedule any required inspections, especially for older or commercial vehicles



Related Post
Frontier Terminal Sfo A Comprehensive Guide To Navigating The Airport

Unlocking Patreon Content: A Simple Guide to Downloading with Clarity and Confidence

Full Body Pilates With Weights Move With Nicole: Transform Your Strength, Flexibility, and Mind-Body Connection
KSTVET School Fees: A Simple, Clear Guide for Every Parent and Student

