Master the Double Elimination Tournament Bracket: The Ultimate Guide to Winning Structure and Strategy
Master the Double Elimination Tournament Bracket: The Ultimate Guide to Winning Structure and Strategy
In the world of competitive arenas, few formats command the intensity and tactical depth of the double elimination tournament bracket. Far more complex than a standard single-elimination setup, this structure rewards persistence and adaptability, delivering memorable moments and high-stakes drama. Used across sports, gaming, and esports, the double elimination format ensures no team or player advances without proving their resilience—losing once doesn’t mean gone, but eventual passage demands mastery of both win-loss precision and strategic recovery.
Understanding the inner mechanics of this bracket is essential for participants, coaches, and fanatics alike.
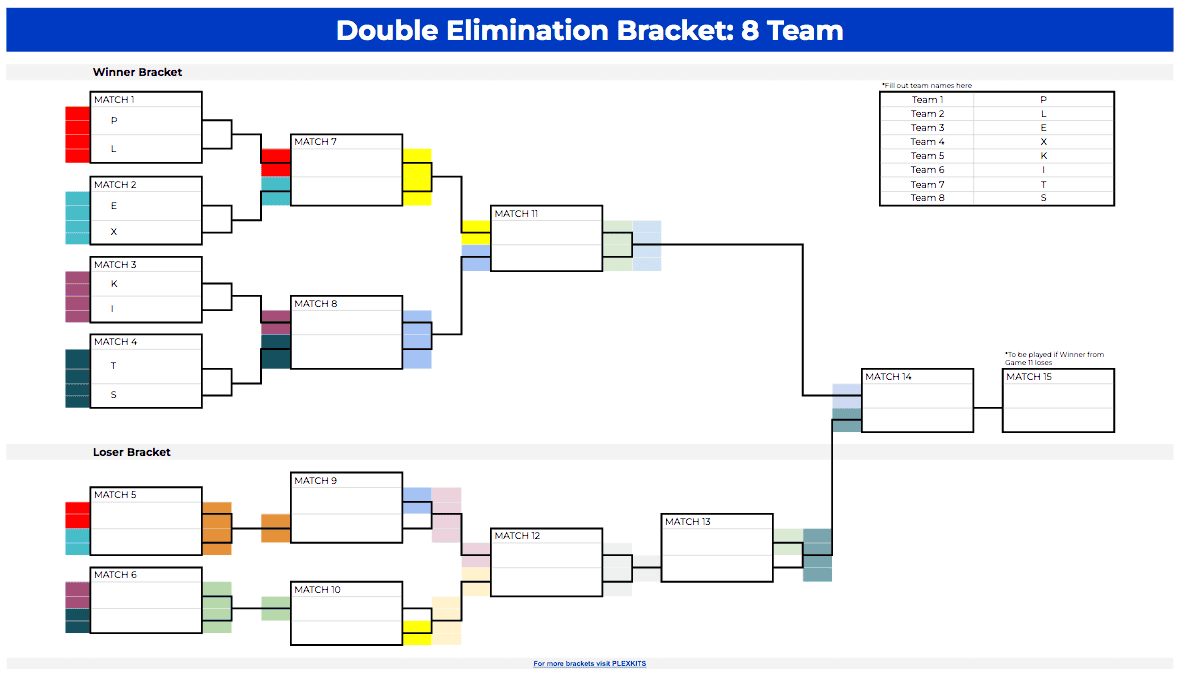
At its core, a double elimination bracket is designed to eliminate a team only after two consecutive losses, creating a binary phase where early setbacks don’t immediately conclude a run. The structure consists of two "lives": the Victory Lane (or Leader’s Bracket), where undefeated teams push forward, and the Death Room (or Losers’ Bracket), where teams eliminated in the first round regroup only when beaten again.
This dual-path system creates a dynamic unfinished narrative, with potential rematches injecting unpredictability and emotional tension into every match. For competitors, this means defending gains aggressively and maintaining mental sharpness across multiple windows of opportunity.
Each round in a double elimination bracket is defined by three key stages:
- Opening Round:** Teams enter the bracket in structured seeding, often determined by prior rounds or direct melt picks. The first matchups set momentum, with powerhouses frequently face-to-for-mouth in early elimination bouts.
- Elimination and Revival Points:** After each loss, a team enters the Death Room—unless the format ends in one final match. Here, losses are impactful but reversible, demanding tactical resilience.
- Final Sudden Death or Final Match:** The last survival team faces off in a decisive encounter, often determined by random draw or highest skill-seeded advantage, crowning the ultimate champion.
- Elimination and Revival Points:** After each loss, a team enters the Death Room—unless the format ends in one final match. Here, losses are impactful but reversible, demanding tactical resilience.
The double elimination model stands apart from other formats due to its tolerance for error and capacity for comeback stories, making it a fan favorite in high-stakes environments.
Compared to single elimination—where a single failure ends a run—this structure fosters deeper engagement, as teams must balance aggression with long-term strategy. In NCAA basketball tournaments, for example, the double elimination bracket allows teams a fallback path, preserving competitive integrity while amplifying drama. “This format puts psychological pressure in context—not every para from the start, but every win matters,” noted sports analyst Sarah Chen.
“It’s not just about winning round one; it’s about surviving a full pass.”
Structure of a Double Elimination Bracket
The foundation of any double elimination setup lies in its geometric design. Typically drawn as a symmetrical ladder with parallel paths—the Victory Lane and Death Room—each team follows a linear path until elimination. Seeds are usually distributed uniformly to prevent top-tier teams colliding too early, ensuring balanced progression.
The bracket’s progression follows a predictable pattern but gains complexity through back-and-forth rebounds when a team loses. Standard formats use a 2-kill rule: a team must lose two matches to exit, skipping only one rematch under most structured systems.
Key Structural Components: - **Parent Bracket (Victory Lane):** Unrestricted path to final victory; exempt from immediate elimination.
- **Death Room (Losers’ Bracket):** Open only to teams losing once; elimination occurs only after a second defeat. - **Advancement Triggers:** Victory in any round resets a team to the top of its lane; loss moves a team to the Death Room. - **Termination Condition:** The final match only occurs when both lanes are fully cleared; no match occurs without a conclusive champion.
- **Seeding Logic:** Seeds are assigned based on prior performance or randomized placement to avoid early, disruptive encounters.
This structure ensures every defeat remains reversible, creating incentives for aggressive play but rewarding patience and resilience. In esports tournaments such as League of Legends’ double or solo queue formats, this dual survival system transforms defeat into strategic opportunity, keeping both players and spectators deeply invested throughout the tournament lifecycle.
The operational logic extends beyond structure into how brackets are populated. Seeding typically uses a combination of current rankings, past performance, and sometimes directional drops to maintain competitive fairness. National collegiate tournaments often seed by conference or national performance, minimizing early mismatches between elite and emerging



Related Post

Davi Lucca Redefines Digital Leadership: The Architect Behind Tesla’s Creative Firepower

Chef Esther Choi Husband: Mastering Culinary Excellence with Heart and Vision

Fermn: The Revolutionary AI That’s Redefining Efficiency in Modern Technology
Arch Manning Stats: Decoding the Freshman Quarterback's Initial Impact at Texas

