Hydroboration-Oxidation: The Gateway to Alkenes with Unmatched Synthetic Power
Hydroboration-Oxidation: The Gateway to Alkenes with Unmatched Synthetic Power
Pivotal to modern organic synthesis, the hydroboration-oxidation reaction remains a cornerstone strategy for converting alkenes into alkanes with controlled stereochemistry—delivering precision rarely matched by alternative methods. This elegant two-step process transforms electron-rich double bonds into functionalized single bonds through selective borane addition followed by oxidative conversion, enabling chemists to build complex molecules with high efficiency and reliability. Far more than a routine transformation, it exemplifies the synergy between molecular reactivity and deliberate electron flow, making it indispensable in pharmaceuticals, materials science, and academic research.
### The Mechanism: From Boron Hydride to Defined Alcohol At its core, the hydroboration-oxidation sequence begins with hydroboration—where a borane species, typically borane (BH₃) or a stabilized borane like 9-BBN, adds across an alkene’s π-bond. This selective addition follows anti-Markovnikov regioselectivity, meaning the boron atom attaches to the less substituted carbon, while hydrogen bonds to the more substituted carbon. This counterintuitive selectivity arises from the concerted, cyclic transition state involving simultaneous B-H bond formation and C-H cleavage.
The result is a vinyl borane intermediate with boron positioned like a silent guide for the next step. Oxidation then transforms this intermediate into a targeted alcohol. When treated with hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) in a basic medium—often sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide—both boron and hydrogen are replaced by a hydroxy group (–OH).
The role of peroxide is crucial: it delivers oxygen atom transport without over-oxidizing to carbonyls or disrupting stereochemistry. The final product is an alcohol with terminal—rather than vicinal—hydroxy placement, a stereochemical signature that distinguishes it from other oxidations. “What makes hydroboration-oxidation truly special is the predictability of its outcome,” notes Dr.
Elena Torres, a synthetic organic chemist at MIT. “Unless otherwise directed, the boron always adds to the terminal end of the alkene, and the resulting alcohol maintains anti-Markovnikov configuration—something not guaranteed with peroxide-based oxidations alone.” ### Regioselectivity and Stereochemistry: Precision Engineered The reaction’s razor-sharp regioselectivity stems from electronic and steric factors. The pi electrons of the alkene attack the borane’s electron-deficient boron, while the δ bond between boron and carbon partially breaks, positioning the hydrogen to add to the carbon with higher substitution.
This anti-Markovnikov effect ensures that the larger substituent remains on the newly formed single bond, a feature exploited in synthesizing functionalized alcohols essential to drug development. Stereochemistry is equally controlled. Because the addition occurs in a synchronous process without bond breaking on the carbon framework, the geometry at the new carbon center—syn addition—preserves stereochemical fidelity.
For unsubstituted alkenes, this yields racemic mixtures at asymmetric centers; for chiral alkenes, it generates defined stereochemical outcomes. This predictability enables total synthesis of complex natural products where alcohol placement determines biological activity. ### Practicality and Versatility: A Must-Have Tool One of hydroboration-oxidation’s greatest strengths lies in its operational simplicity and functional group tolerance.
Unlike many alkene functionalizations that demand harsh conditions or expose sensitive moieties to damage, this reaction proceeds under mild, neutral-to-slightlyBasic conditions. Oxidants like H₂O₂ are benign, generating water as a byproduct—aligning with green chemistry principles. The versatility extends to substrate range.
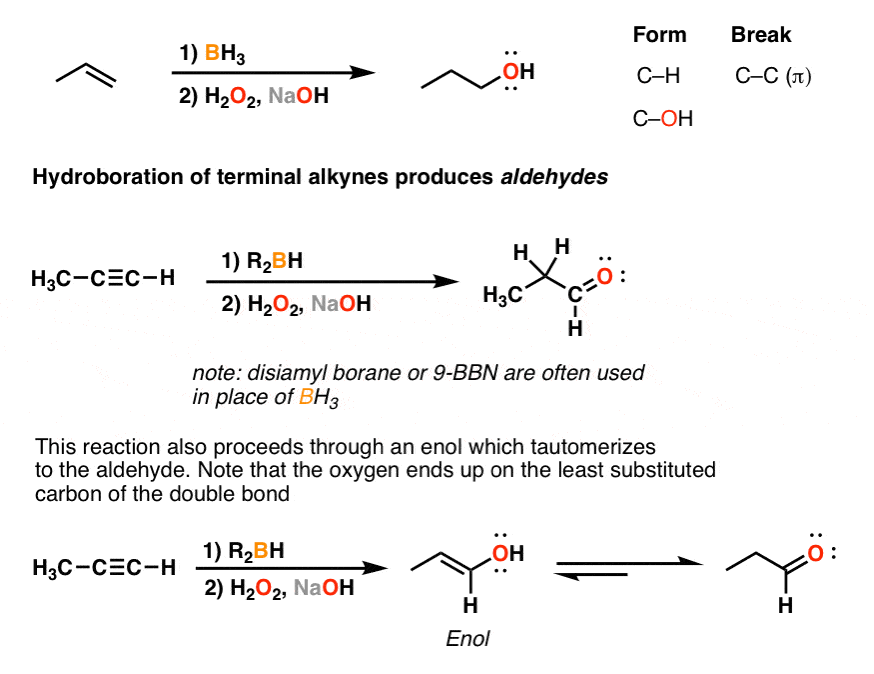
Primary and secondary alkenes react efficiently; terminal alkynes undergo a similar transformation (cyanohydrin formation) when borane adds to the triple bond first. Even sensitive functional groups such as esters, ethers, and nitriles survive oxidation, making the method broadly applicable across diverse molecular architectures. In pharmaceutical synthesis, where stereochemical control and purity are paramount, hydroboration-oxidation serves as a key step in preparing intermediates for active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).
Its ability to install hydroxyl groups at precise positions without racemization ensures downstream transformations proceed with minimal purification hurdles. ### Challenges and Optimization in Practice Despite its strengths, mastering hydroboration-oxidation demands careful attention to reagent stoichiometry and reaction conditions. Borane is highly reactive and air-sensitive, requiring inert atmosphere handling and fresh solutions.
Excess borane can lead to over-addition or side reactions, while insufficient amounts result in incomplete conversion. Careful control of loading—typically a 1:1 molar ratio—ensures optimal outcome. Worksheet protocols often recommend octane or diisopropyl ether as solvent, with additives like THF to stabilize borane and suppress side oxidation.
Monitoring reaction progress via TLC or GC remains essential to prevent decomposition, especially during prolonged exposure. Moreover, stereochemical control demands awareness of alkene configuration: cis-trans (E/Z) isomers may yield different products depending on steric crowding near the reaction site. In cases where absolute stereocontrol is required, chiral borane reagents—though less common—are available, albeit at increased cost and complexity.
### Applications: From Lab to Industry The real-world reach of hydroboration-oxidation spans multiple sectors. In medicinal chemistry, it facilitates the late-stage functionalization of drug candidates, enabling rapid analog synthesis for structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies. For example, the anti-inflammatory drug celecoxib benefits from this transformation in constructing its critical alcohol functionality.
In materials science, hydroboration-oxidation aids in tailoring oligomers and polymers with defined end-groups, influencing solubility, reactivity, and chain mobility. Conjugated systems derived via this route serve as building blocks in organic electronics and photovoltaic materials. Academic labs use the reaction to probe fundamental reaction mechanisms, with mechanistic studies confirming the concerted nature of borane addition and oxidative hydrogenation.
Its role in stereoselective synthesis continues to inspire novel catalyst designs, aiming to expand compatibility with heteroatom-substituted alkenes and improve atom economy. In industrial settings, scalability considerations shape process development. Continuous flow reactors, borrowed from pharmaceutical manufacturing, enhance safety and yield by precisely controlling borane dosing and residence time—critical when handling reactive borane complexes.
### The Unwavering Role of Hydroboration-Oxidation Hydroboration-oxidation stands as a paragon of efficiency and precision in organic synthesis. By leveraging borane’s unique reactivity and harnessing peroxide-assisted oxidation, it delivers controlled regio- and stereochemical outcomes—attributes that no alternative alkene transformation yet rivals. The reaction’s enduring value lies not only in its utility across synthesis but in its role as a blueprint for designing selective, predictable, and scalable transformations.
Whether designing life-saving therapeutics, engineering advanced materials, or unraveling molecular mechanisms, chemists rely on this two-step classic as a dependable partner. It exemplifies how fundamental chemical transformations, refined over decades, remain vital in an era of innovation. In the evolving landscape of synthetic chemistry, hydroboration-oxidation endures as more than a reaction—it is a strategic choice, a testament to elegance, and a testament to the power of thoughtful molecular design.



Related Post

Hydroboration Oxidation: The Molecular Alchemy Behind Hydrocarbon Transformations
Jennifer Lambers FOX 10 Bio Wiki Age Height Family Husband Salary Net Worth
Unlocking the Secrets of Cuban Oregano: Your Essential Guide to Culinary Uses, Health Benefits, and More

Rio Ferdinand Net Worth: A Deep Dive Into the Financial Legacy of a Football Icon

