From Megabytes to Kilobytes: Decoding 15MB’s True Size in Real-World Terms
From Megabytes to Kilobytes: Decoding 15MB’s True Size in Real-World Terms
Understanding data conversion is essential in an era where digital information flows seamlessly across networks, storage devices, and devices. One of the most commonly referenced units in this domain is the megabyte (MB) — a unit representing 1 million bytes — and its smaller cousin, the kilobyte (KB), equivalent to 1,000 bytes in the decimal system. This article breaks down exactly how 15 megabytes translates into kilobytes and why this conversion matters in everyday computing, networking, and digital storage.
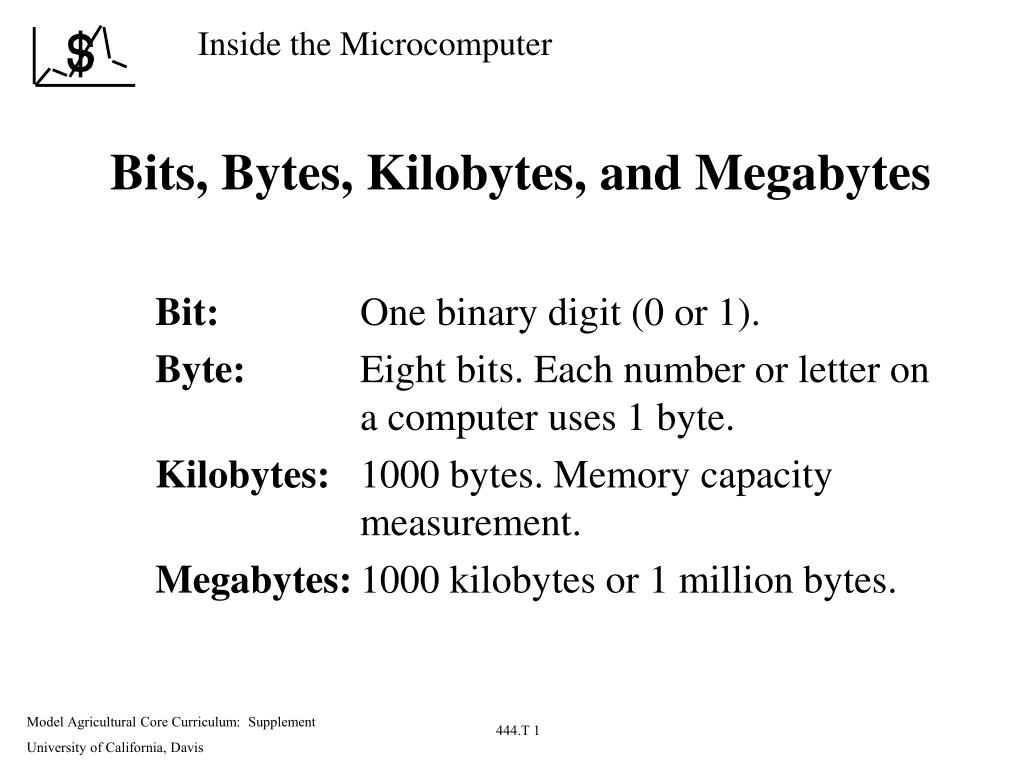
The core relationship lies in the prefix system: 1 MB equals 1,000 KB. This standard, maintained by SI (International System of Units) conventions, allows precise digital measurement. Therefore, converting 15 MB to KB is a matter of simple multiplication: 15 MB × 1,000 KB/MB = 15,000 KB.
This means 15 megabytes equals exactly 15,000 kilobytes — a clear, quantifiable scale.
In real-world applications, this conversion bridges gaps between abstract data sizes and tangible storage capacities. For instance, a high-resolution photo or a short HD video clip typically ranges from 2 to 15 MB.
Breaking this down, a 12 MB image occupies approximately 12,000 KB — a figure that shapes how users manage photo libraries and cloud backups. When downloading or uploading, understanding that 15 MB translates directly to 15,000 KB ensures users accurately allocate bandwidth and storage space, avoiding estimate-based miscalculations.
Why KB and MB Matter in Computing and Communication
KB and MB serve as foundational metrics across digital ecosystems. They simplify communication of file sizes, network throughput, and memory capacity, all crucial in both consumer and enterprise contexts.- **File Management:** Operators and users rely on MB-to-KB conversion to estimate storage needs. A 500 MB file — roughly 500,000 KB — requires careful placement in folders or cloud accounts with limited space. - **Network Performance:** Internet speeds are often quoted in Mbps (megabits per second), but underlying data transfer hinges on bytes.
Converting these into KB helps quantify download or upload times—say, transferring a 7.5 MB file across a 10 Mbps connection demands precise knowledge of 7,500 KB divided by 10,000, yielding 0.75 seconds per megabit. - **Software Development:** Programmers and engineers use KB and MB units to benchmark resource consumption — from embedded systems with tight memory constraints to large-scale data operations in cloud platforms.
The precision provided by 15 MB = 15,000 KB extends beyond utility; it enables efficient planning and resource optimization, preventing bottlenecks in data handling processes.
The Anatomy of Storage: Comparing 15MB to Everyday Files
Breaking 15 MB into kilobytes offers tangible reference points.For context: - About 150 standard email attachments (1 MB each) fill 150 MB — roughly 150,000 KB, illustrating how quickly megabytes accumulate. - A typical MP3 music file hovers around 3–5 MB, meaning 15 MB supports 3 to 5 full songs — a common benchmark for portable device storage. - Video content differs vastly: a 10-second HD clip may use 2–3 MB, translating to 2,000–3,000 KB — a visible slice of total 15 MB.
- In cloud storage tiers, 15 MB could equate to a small folder of documents, photos, or backups, highlighting practical limits for personal or small business use.
These comparative scales underscore that while 15 MB is modest, its precise KB equivalent empowers decision-making across diverse digital activities.
Technical Foundations: From Binary to Decimal Conventions Though 1000 is standard for decimal megabyte and kilobyte definitions, it’s crucial to acknowledge alternative binary conventions, especially in computer architecture. In binary (base-2), 1 KB = 1,024 bytes, and 1 MB = 1,048,576 bytes — leading to 1 MB = 1,000,000 bytes and 1 GB = 1,000,000,000 bytes.
Despite this, most consumer devices and internet services adhere to decimal metrics for consistency. This decimal approach directly affects how 15 MB translates: 15 MB = 15 × 1,000 = 15,000 KB versus 15 MB = 15 × 1,024² ≈ 15,728,640 bytes ≈ 15,360 KB (if using 1 KB = 1,024 bytes), but only when strict binary standards apply. In everyday contexts, however, 15,000 KB remains the widely accepted metric.
This uniformity ensures accurate alignment between user interfaces, storage hardware, and network tools — a critical factor in digital reliability and transparency.
Implications for Digital Literacy and User Empowerment
Understanding MB-to-KB conversion equips users to navigate digital life with clarity and control. When managing storage, planning downloads, or troubleshooting transfer issues, the ability to convert 15 MB to 15,000 KB transforms abstract numbers into actionable knowledge. Educational initiatives and tech literacy programs increasingly emphasize such conversions, reinforcing how numerical fluency enhances digital agency.Whether organizing photo archives, downloading educational resources, or optimizing workflows, precise knowledge of data sizing empowers users to make informed choices. Moreover, in professional environments — from IT departments managing servers to content creators distributing media — standardized data measurements ensure consistency and prevent costly miscalculations. The translation of 15 MB into 15,000 KB is more than a technical footnote; it is a linchpin of digital competence.
In an era dominated by data, clarity often resides in the smallest


Related Post
Watson Cream For Hemorrhoids: Finding Relief and Understanding Treatment Options

Liban: Where Ancient Civilizations Collide with Modern Innovation
Vince McMahon Once Told Triple H That Rhino Would Never Work for WWE Again
Eugene Robinson Washington Post Bio Wiki Age Height Wife Sons MSNBC Salary and Net Worth

