Decode Molecular Geometry with the Pogil Answer Key: Master Shapes That Define Chemistry
Decode Molecular Geometry with the Pogil Answer Key: Master Shapes That Define Chemistry
The Molecular Geometry Pogil Answer Key stands as an indispensable tool for students and educators navigating the complex world of molecular shape theory. By aligning atomic layout with conceptual understanding, this resource translates abstract VSEPR principles into tangible learning outcomes, enabling precise prediction of molecular structures that govern reactivity and function. Its structured approach—rooted in observable electron pair repulsion—transforms theoretical frameworks into practical mastery.
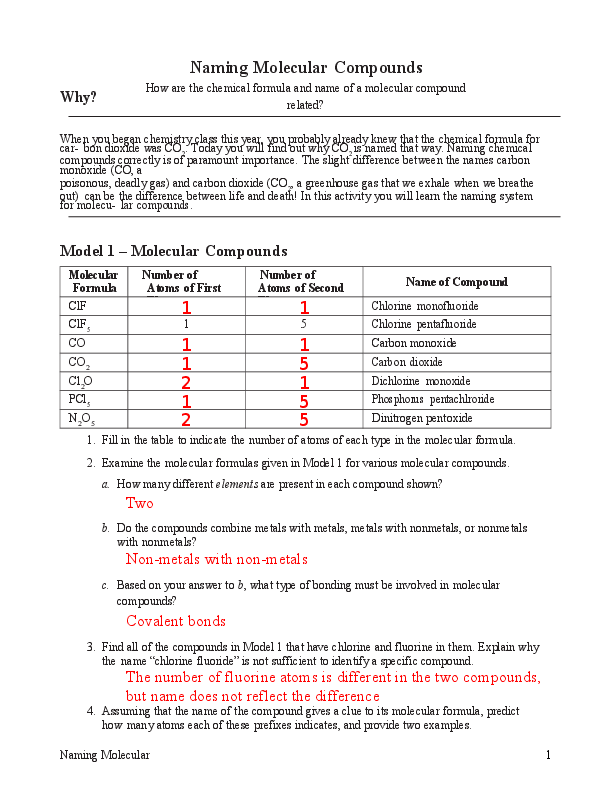
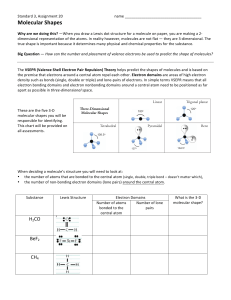
At the core of molecular geometry lies the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) model, a cornerstone concept in chemistry that explains how electron domains around a central atom dictate three-dimensional structure. The Pogil Answer Key refines this model through targeted questioning, guided transitions, and evidence-based reasoning, helping learners identify bond angles, molecular symmetry, and physical properties tied directly to shape. As one answer emphasizes, “Geometry isn’t just about images—it’s the language of molecular behavior.” This integration of theory and application ensures students don’t just memorize facts but internalize how molecular geometry influences everything from gas solubility to drug-receptor binding.
Central Principles of Molecular Shape: Electron Pairs and Repulsion
The VSEPR theory rests on a simple yet powerful premise: electron pairs—bonding and lone—repel one another, positioning themselves to minimize this strain. The Molecular Geometry Pogil Answer Key breaks this down with clarity, guiding students through step-by-step evaluation of central atoms, bonding pairs, and non-bonding electrons. Each answer set emphasizes: - Identification of electron domain counts at the core atom.- Differentiation between bonding pairs (shared between atoms) and lone pairs (localized on central atoms). - Prediction of hybridization states and coordination geometry. - Translation of electron repulsion into molecular geometry—be it linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, or more complex forms.
For example, a molecule with four bonding pairs and no lone pairs adopts a tetrahedral arrangement, with an ideal bond angle of 109.5°. The Pogil guides learners to assess such configurations systematically, reinforcing the idea that geometry arises from electron distribution.
Tests reveal that students often struggle with distinguishing between electron domains and actual molecular shape.
The answer key addresses this by highlighting common pitfalls: a molecule with five total electron domains may form a trigonal bipyramidal structure only when lone pairs occupy equatorial or axial positions to minimize replacement. This nuance is critical—lone pairs exert stronger repulsion than bonding pairs, distorting ideal angles. The Pogil’s flowchart-style prompts help learners visualize these interactions, turning confusing scenarios into solvable problems.
Applications of Molecular Geometry: From Reactivity to Real-World Impact
Understanding molecular shape is far more than an academic exercise—it directly influences chemical reactivity, polarity, phase behavior, and biological function.The Pogil Answer Key bridges this gap by illustrating how geometry affects: - Bond angles that determine molecular polarity and intermolecular forces. - Steric hindrance influencing reaction mechanisms. - The three-dimensional fit required for enzyme-substrate interactions in biochemistry.
- Solubility and transport properties in aqueous and nonpolar environments.
As one answer asserts, “Geometry isn’t static; it responds to electron distribution, and the Pogil teaches you to read these subtle signals.”
Another critical dimension highlighted is molecular deformation under strain. Double bonds and lone pairs occupy more spatial volume than single bonds, compressing nearby angles and altering symmetry. The Pogil guides learners to detect such deviations, mapping out real-world examples: water’s bent structure (104.5° bond angle vs.
ideal 109.5°) stems from lone pair compression in oxygen. This level of detail transforms abstract theory into observable reality.
Mastering Geometry Through Structured Practice and Feedback
The Pogil Answer Key excels in transforming passive study into active engagement.Exercises are designed to scaffold learning: starting with simple molecules like methane (CH₄) to reinforce tetrahedral geometry, progressing to trigonal bipyramidal and octahedral configurations, and culminating in complex cases involving expanded octets (e.g., SF₆). Each question pair includes: - Clear instructions linking atomic arrangements to molecular identity. - Feedback mechanisms such as diagram labeling and angle prediction.
- Opportunities to defend predictions using scientific reasoning. This iterative approach fosters deeper retention. For example, when asked to draw the shape of sulfur hexafluoride (SF₆), learners must identify six bonding pairs around sulfur, enabling a octahedral geometry—one of the most symmetrical in chemistry.
The Pogil answers confirm this structure as the most stable, aligning with theory and observation.
Importantly, the Answer Key encourages error analysis. Instead of merely marking answers right or wrong, it prompts learners to: Visualize electron pair repulsions, Calculate bond angles, and Justify structural choices.
This metacognitive layer strengthens analytical skills vital for research and professional chemistry.
Why the Pogil Approach Reshapes Chemistry Education
The Molecular Geometry Pogil Answer Key represents a paradigm shift in learning—transforming abstract concepts into interactive, testable models. By integrating guided inquiry with rigorous accuracy, it equips students to not only understand but anticipate molecular behavior. Its focus on spatial reasoning, electron dynamics, and real-world relevance ensures that geometry becomes intuitive, not intimidating.As educators and learners engage with this resource, the message becomes clear: molecular geometry is not an esoteric subtopic, but the foundational chapter in mastering chemical identity. It governs solubility, reactivity, and even shape-defined functions in pharmaceuticals, materials science, and biology. And with the Pogil Answer Key leading the way, every question answered deepens insight—and every diagram drawn becomes a window into the invisible architecture of matter.
In a discipline where form dictates function, understanding molecular geometry is mastering the blueprint of chemical life. The Pogil Answer Key doesn’t just guide answers—it shapes how learners perceive and interact with the molecular world.


Related Post
Unpacking the Politics of the Pen: Is Kendrick Lamar A Democrat Or Republican? The Evidence Behind the Enigma

Asian Twerk: From Niche Dance Movement to Global Cultural Phenomenon

Discover Enchanting Farm Names for Stardew Valley: Where Every Plot Holds Magic
Trailblazing Findings from Nelson's Exploration

