37℃ to °F: The Precision Temperature Conversion That Changes Understanding
37℃ to °F: The Precision Temperature Conversion That Changes Understanding
Converting 37°C to Fahrenheit is far more than a routine calculation — it’s a gateway to grasping how temperature scales shape weather forecasts, health monitoring, and global climate science. At its core, this conversion reveals critical insights about human biology, environmental responses, and technical applications. Knowing that 37°C equals 98.6°F isn’t just a trivia fact; it establishes a universal benchmark that bridges everyday experience and scientific accuracy.
Understanding this conversion demands more than rote memorization — it requires insight into the underlying mathematics and real-world relevance. The process relies on a precise mathematical formula, a scale rooted in historical conventions, and applications that span medicine, meteorology, and engineering. Without this knowledge, interpreting temperature data risks inaccuracy, miscommunication, and flawed decision-making in fields where precision matters.
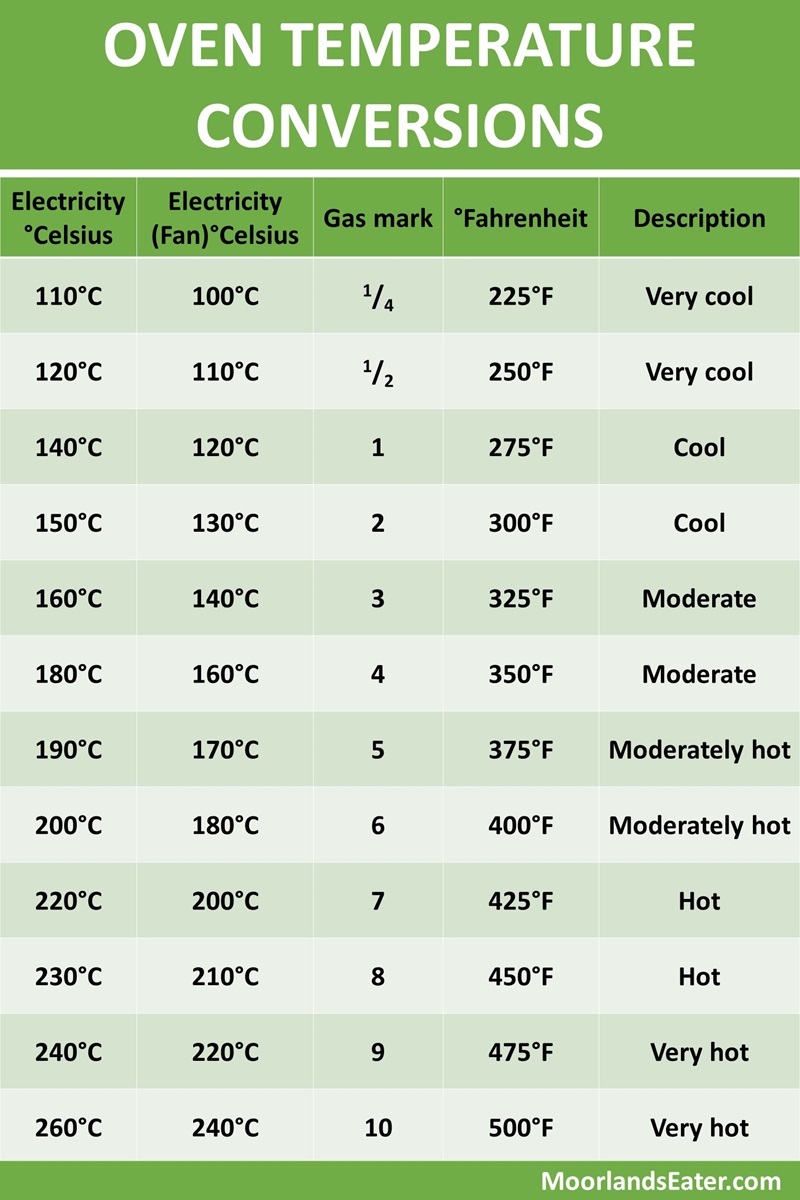
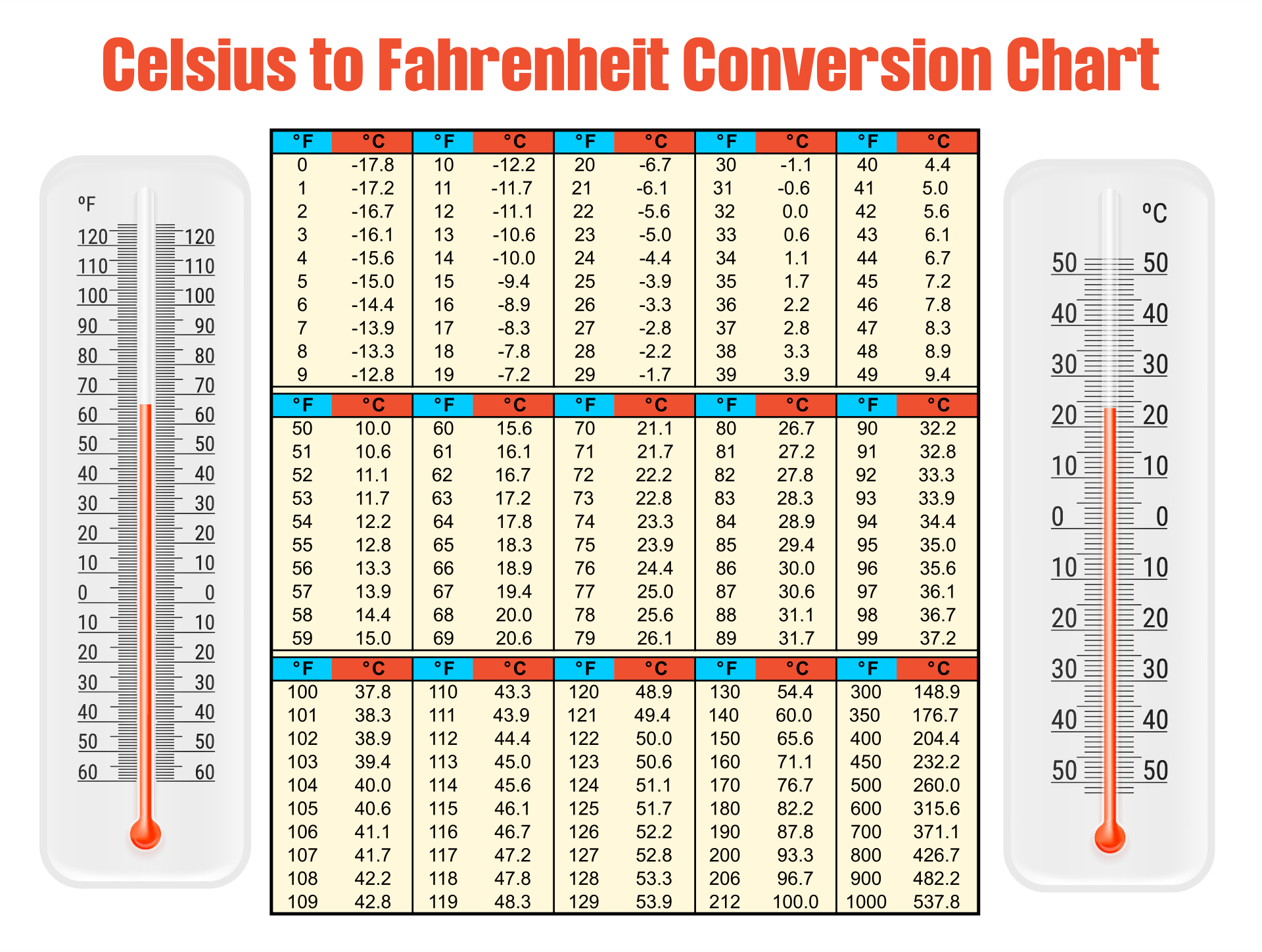
To transform a temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit, the official formula applies: × 9⁄5, then +32. This mathematical framework emerged from the need to unify disparate thermal measurement systems. The °C scale, developed in the 18th century by Anders Celsius, assigns water’s freezing and boiling points as reference milestones, while the °F scale, formalized earlier by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit, uses a different reference system—originally based on brine solutions and human thermal perception.
Despite these divergent origins, the conversion remains mathematically exact, ensuring consistency across scientific and technical domains.
Mathematical Precision Behind the Conversion
The conversion formula—°F = (°C × 9⁄5) + 32—serves as the foundation for all temperature transformations between these scales. Grasping each component reveals the depth of its scientific design: - The multiplier 9⁄5 arises from the fact that every degree Celsius encompasses 9⁄5 degrees Fahrenheit in temperature interval, reflecting the non-linear relationship between Celsius and Fahrenheit units. - Adding 32 shifts the zero point: while 0°C marks water’s freezing, 32°F is roughly 0°C, bridging the scales at this fixed reference.- Empirical validation confirms the formula’s reliability, with deviations under 0.01°F even at extreme temperatures, affirming its readiness for use in high-stakes environments. This precision supports critical applications, from calibrating medical thermometers to fine-tuning climate models that predict global weather patterns.
What does 37°C truly mean in Fahrenheit, and why does this number matter? At exactly 37°C, the temperature corresponds to a resembling human body temperature—98.6°F—a pivotal benchmark in medicine and physiology.
This equilibrium illustrates how thermometers rely on this precise transition point to deliver clinically relevant readings. When patients run fevers or experience hypothermia, temperature displays grounded in this conversion guide accurate diagnosis and timely treatment. Beyond individual health, this conversion drives public understanding of climate data.
Meteorologists depend on Fahrenheit conversions during extreme heatwaves or cold snaps to communicate risks clearly across regions. For example, a forecast of 37°C translates directly to 98.6°F, making warnings more intuitive: “Extreme heat approaching—watch for heat exhaustion,” a message far more relatable when tied to body-temperature equals.
Applications Across Science and Technology
Temperature conversion underpins disciplines where precision is non-optional.- **Meteorology**: Weather models integrate converted temperatures to simulate atmospheric dynamics, improving storm tracking and climate trend analysis. - **Industrial Engineering**: Chemical processes require exact thermal control; converting 37°C (the typical human body temperature) ensures equipment operates safely within regulatory limits. - **Space Exploration**: Sensors on spacecraft monitor extreme environments, with data converted to Fahrenheit for real-time decisions during launch and planetary operations.
Each context demands exactness—no approximation, no rounding—reinforcing why 37°C to °F is not just a calculation, but a critical operational standard.
Avoiding Pitfalls in Temperature Conversion
While the formula is straightforward, misunderstandings persist. A common error is skipping the 9⁄5 multiplier and instead averaging or doubling differences, which introduces errors up to 0.5°F in extreme ranges.Similarly, misremembering the +32 shift leads to drastic inaccuracies—critical in settings like food safety or HVAC calibration where deviations risk health or structural integrity. To ensure accuracy, professionals follow a third-step verification: 1. Apply °C × 9⁄5 2.
Add 32 3. Cross-check with trusted sources (e.g., NIST or standardized thermometer calibrations)
This discipline ensures that every conversion supports sound judgment and safe action. The Broader Implications of a Simple Conversion
Understanding 37°C to °F unlocks more than a single temperature figure—it reveals how standardized scales transform data into actionable knowledge.
From alerting doctors to fever patterns to guiding seasonal agricultural planning, this conversion bridges scales to serve real-world needs. In a world increasingly shaped by climate data and personal health tracking, such transformations remain foundational to modern life. In essence, converting 37°C to 98.6°F is not merely a mathematical exercise—it is a gateway to clearer thinking, better decisions, and deeper trust in scientific information.
This precise conversion exemplifies how standardized units, though invisible in daily use, are essential to global communication, safety, and innovation.

Related Post

37°C to Fahrenheit: The Exact Conversion That Powers Science, Travel, and Everyday Decisions
Who Is Benni From The Queen Actress

Nigeria’s National Identity: Threads of Diversity Woven into a Shared Future

